Rhodococcus equi secreted antigens are immunogenic and stimulate a type 1 recall response in the lungs of horses immune to R. equi infection
- PMID: 14573652
- PMCID: PMC219552
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.11.6329-6337.2003
Rhodococcus equi secreted antigens are immunogenic and stimulate a type 1 recall response in the lungs of horses immune to R. equi infection
Abstract
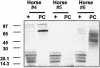
Rhodococcus equi is an opportunistic pathogen in immunocompromised humans and an important primary pathogen in young horses. Although R. equi infection can produce life-threatening pyogranulomatous pneumonia, most foals develop a protective immune response that lasts throughout life. The antigen targets of this protective response are currently unknown; however, Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a closely related intracellular pathogen and provides a model system. Based on previous studies of M. tuberculosis protective antigens released into culture filtrate supernatant (CFS), a bacterial growth system was developed for obtaining R. equi CFS antigens. Potential immunogens for prevention of equine rhodococcal pneumonia were identified by using immunoblots. The 48-h CFS contained five virulence-associated protein bands that migrated between 12 and 24 kDa and were recognized by sera from R. equi-infected foals and immune adult horses. Notably, the CFS contained the previously characterized proteins VapC, VapD, and VapE, which are encoded by genes on the R. equi virulence plasmid. R. equi CFS was also examined for the ability to stimulate a type 1-like memory response in immune horses. Three adult horses were challenged with virulent R. equi, and cells from the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were recovered before and 1 week after challenge. In vitro stimulation of pulmonary T-lymphocytes with R. equi CFS resulted in significant proliferation and a significant increase in gamma interferon mRNA expression 1 week after challenge. These results were consistent with a memory effector response in immune adult horses and provide evidence that R. equi CFS proteins are antigen targets in the immunoprotective response against R. equi infection.
Figures


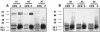
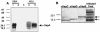
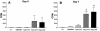
Similar articles
-
Immunity to Rhodococcus equi: antigen-specific recall responses in the lungs of adult horses.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001 May 10;79(1-2):101-14. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(01)00258-6. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001. PMID: 11356253
-
Clearance of virulent but not avirulent Rhodococcus equi from the lungs of adult horses is associated with intracytoplasmic gamma interferon production by CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003 Mar;10(2):208-15. doi: 10.1128/cdli.10.2.208-215.2003. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12626444 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental infection of neonatal foals with Rhodococcus equi triggers adult-like gamma interferon induction.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Jun;14(6):669-77. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00042-07. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17409222 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and virulence of Rhodococcus equi.Vet Microbiol. 1997 Jun 16;56(3-4):257-68. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(97)00094-1. Vet Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9226840 Review.
-
Current understanding of the equine immune response to Rhodococcus equi. An immunological review of R. equi pneumonia.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010 May 15;135(1-2):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2009.12.004. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 20064668 Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental Rhodococcus equi and equine infectious anemia virus DNA vaccination in adult and neonatal horses: effect of IL-12, dose, and route.Vaccine. 2007 Oct 23;25(43):7582-97. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.07.055. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17889970 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of neutrophils in mice experimentally infected with Rhodococcus equi.Infect Immun. 2005 Oct;73(10):7040-2. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.7040-7042.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16177388 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodococcus equi-infected macrophages are recognized and killed by CD8+ T lymphocytes in a major histocompatibility complex class I-unrestricted fashion.Infect Immun. 2004 Dec;72(12):7073-83. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.7073-7083.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15557631 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Administration of Electron-Beam Inactivated Rhodococcus equi Failed to Protect Foals against Intrabronchial Infection with Live, Virulent R. equi.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 1;11(2):e0148111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148111. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26828865 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of vaccine candidates against Rhodococcus equi in BALB/c mice infection model: cellular and humoral immune responses.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jul 8;24(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03408-z. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38977999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen, P. 1994. The T cell response to secreted antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Immunobiology 191:537-547. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, P., A. B. Andersen, A. L. Sorensen, and S. Nagai. 1995. Recall of long-lived immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection mice. J. Immunol. 154:3359-3372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

