Role of cytokines and major histocompatibility complex restriction in mouse resistance to infection with a natural recombinant strain (type I-III) of Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 14573660
- PMCID: PMC219541
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.11.6392-6401.2003
Role of cytokines and major histocompatibility complex restriction in mouse resistance to infection with a natural recombinant strain (type I-III) of Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
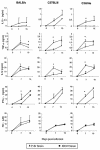
Herein we characterized various genetic markers and the biological behavior of a natural recombinant strain of Toxoplasma gondii (P-Br). From nine genetic markers analyzed, three (B1, ROP1, and SAG1) and three (cS10-A6, GRA6, and SAG3) markers belong to parasites from the type I and type III lineages, respectively. The SAG2 and L363 loci were shown to be type I-III chimera alleles. The cB2l-4 microsatellite marker showed a unique haplotype. The P-Br strain presented low virulence in the acute phase of infection and was cystogenic during the chronic infection. The interleukin 12/gamma interferon axis and inducible nitric oxide synthase were main determinants of resistance during the acute infection with the P-Br strain. As opposed to infection with the type II strain of T. gondii (ME-49), peroral infection with the P-Br strain led only to a light inflammatory infiltrate and no major lesions in the intestine of the C57BL/6 mice. In addition, the BALB/c (resistant to ME-49) and C57BL/6 (susceptible to ME-49) mice were shown, respectively, to be more susceptible and more resistant to cyst formation and toxoplasmic encephalitis when infected with the P-Br strain. Further, the C57BL/KsJ and DBA2/J congenic strains containing major histocompatibility complex (MHC) haplotype "d" were more resistant than the parental strains (C57BL/6 and DBA1/J), when infected with the ME-49 but not with the P-Br strain. Together, our results indicate that resistance to cyst formation and toxoplasmic encephalitis induced during infection with P-Br is not primarily controlled by the MHC haplotype d, as previously reported for type II strains of T. gondii.
Figures

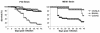


Similar articles
-
The role of MHC haplotypes H2d/H2b in mouse resistance/susceptibility to cyst formation is influenced by the lineage of infective Toxoplasma gondii strain.An Acad Bras Cienc. 2008 Mar;80(1):85-99. doi: 10.1590/s0001-37652008000100005. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2008. PMID: 18345378
-
Influence of genes within the MHC on mortality and brain cyst development in mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii: kinetics of immune regulation in BALB H-2 congenic mice.Parasite Immunol. 1993 Jun;15(6):317-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1993.tb00616.x. Parasite Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8361774
-
Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase exacerbates chronic cerebral toxoplasmosis in Toxoplasma gondii-susceptible C57BL/6 mice but does not reactivate the latent disease in T. gondii-resistant BALB/c mice.J Immunol. 1999 Mar 15;162(6):3512-8. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10092808
-
[Rudolf-Virchow Prize 1998. Award lecture. Toxoplasmosis: a model infection for studying systemic and intracerebral immune reactions].Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1998;82:9-22. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1998. PMID: 10095413 German.
-
Cell-mediated immunity to Toxoplasma gondii: initiation, regulation and effector function.Immunobiology. 1999 Dec;201(2):240-7. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(99)80064-3. Immunobiology. 1999. PMID: 10631573 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxoplasma gondii soluble tachyzoite antigen triggers protective mechanisms against fatal intestinal pathology in oral infection of C57BL/6 mice.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 24;8(9):e75138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075138. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086456 Free PMC article.
-
Latent toxoplasmosis and olfactory functions of Rh positive and Rh negative subjects.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 27;13(12):e0209773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209773. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30589911 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characteristics, Functional Definitions, and Regulatory Mechanisms for Cross-Presentation Mediated by the Major Histocompatibility Complex: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 22;25(1):196. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010196. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular characterization of surface antigen 3 (SAG3) gene of Toxoplasma gondii RH-IVRI strain.J Parasit Dis. 2012 Oct;36(2):210-4. doi: 10.1007/s12639-012-0107-2. Epub 2012 Mar 24. J Parasit Dis. 2012. PMID: 24082530 Free PMC article.
-
The quality of methods reporting in parasitology experiments.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 30;9(7):e101131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101131. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25076044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blackwell, J. M., C. W. Roberts, and J. Alexander. 1993. Influence of genes within the MHC on mortality and brain cyst development in mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii: kinetics of immune regulation in BALB H-2 congenic mice. Parasite Immunol. 15:317-324. - PubMed
-
- Brown, C. R., C. S. David, S. J. Khare, and R. McLeod. 1994. Effects of human class I transgene on Toxoplasma gondii cyst formation. J. Immunol. 152:4537-4541. - PubMed
-
- Brown, C. R., and R. McLeod. 1990. Class I MHC genes and CD8+ T cells determine cyst number in Toxoplasma gondii infection. J. Immunol. 145:3438-3441. - PubMed
-
- Burnett, A. J., S. G. Short, J. Isaac-Renton, A. King, D. Werker, and W. R. Bowie. 1998. Multiple cases of acquired toxoplasmosis retinitis presenting in an outbreak. Ophthalmology 105:1032-1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

