Modulation of T-cell costimulation as immunotherapy or immunochemotherapy in experimental visceral leishmaniasis
- PMID: 14573667
- PMCID: PMC219611
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.11.6453-6462.2003
Modulation of T-cell costimulation as immunotherapy or immunochemotherapy in experimental visceral leishmaniasis
Abstract
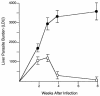
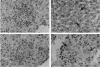
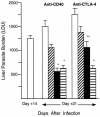
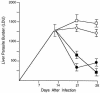
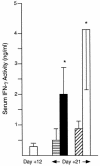
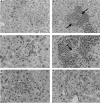
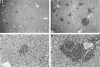
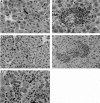
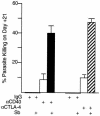
CD40 ligand (CD40L)-deficient C57BL/6 mice failed to control intracellular Leishmania donovani visceral infection, indicating that acquired resistance involves CD40-CD40L signaling and costimulation. Conversely, in wild-type C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice with established visceral infection, injection of agonist anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody (MAb) induced killing of approximately 60% of parasites within liver macrophages, stimulated gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) secretion, and enhanced mononuclear cell recruitment and tissue granuloma formation. Comparable parasite killing was also induced by MAb blockade (inhibition) of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) which downregulates separate CD28-B7 T-cell costimulation. Optimal killing triggered by both anti-CD40 and anti-CTLA-4 required endogenous IFN-gamma and involved interleukin 12. CD40L(-/-) mice also failed to respond to antileishmanial chemotherapy (antimony), while in normal animals, anti-CD40 and anti-CTLA-4 synergistically enhanced antimony-associated killing. CD40L-CD40 signaling regulates outcome and response to treatment of experimental visceral leishmaniasis, and MAb targeting of T-cell costimulatory pathways (CD40L-CD40 and CD28-B7) yields macrophage activation and immunotherapeutic and immunochemotherapeutic activity.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander, J., K. C. Carter, N. Al-Fasi, A. Satoskar, and F. Brombacher. 2000. Endogenous-4 is necessary for effective drug therapy against visceral leishmaniasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 30:2935-2943. - PubMed
-
- Balkhy, H. H., and F. P. Heinzel. 1999. Endotoxin fails to induce interferon-γ in endotoxin tolerant mice: deficiencies in both IL-12 heterodimer production and IL-12 responsiveness. J. Immunol. 162:3633-3638. - PubMed
-
- Belkaid, Y. S., S. Mendez, R. Lira, N. Kadambi, G. Milon, and D. Sacks. 2000. A natural model of Leishmania major infection reveals a profound “silent” phase of parasite amplification in the skin before the onset of lesion formation and immunity. J. Immunol. 165:969-976. - PubMed
-
- Campbell, K. A., P. J. Ovendale, M. K. Kennedy, W. C. Fanslow, S. G. Reed, and C. R. Maliszewski. 1996. CD40 ligand is required for protective cell-mediated immunity to Leishmania major. Immunity 4:283-289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

