Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase activities in bacteria of the Bacillus cereus group
- PMID: 14573681
- PMCID: PMC219565
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.11.6591-6606.2003
Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase activities in bacteria of the Bacillus cereus group
Abstract
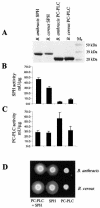
Bacillus anthracis is nonhemolytic, even though it is closely related to the highly hemolytic Bacillus cereus. Hemolysis by B. cereus results largely from the action of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C (PC-PLC) and sphingomyelinase (SPH), encoded by the plc and sph genes, respectively. In B. cereus, these genes are organized in an operon regulated by the global regulator PlcR. B. anthracis contains a highly similar cereolysin operon, but it is transcriptionally silent because the B. anthracis PlcR is truncated at the C terminus. Here we report the cloning, expression, purification, and enzymatic characterization of PC-PLC and SPH from B. cereus and B. anthracis. We also investigated the effects of expressing PlcR on the expression of plc and sph. In B. cereus, PlcR was found to be a positive regulator of plc but a negative regulator of sph. Replacement of the B. cereus plcR gene by its truncated orthologue from B. anthracis eliminated the activities of both PC-PLC and SPH, whereas introduction into B. anthracis of the B. cereus plcR gene with its own promoter did not activate cereolysin expression. Hemolytic activity was detected in B. anthracis strains containing the B. cereus plcR gene on a multicopy plasmid under control of the strong B. anthracis protective antigen gene promoter or in a strain carrying a multicopy plasmid containing the entire B. cereus plc-sph operon. Slight hemolysis and PC-PLC activation were found when PlcR-producing B. anthracis strains were grown under anaerobic-plus-CO(2) or especially under aerobic-plus-CO(2) conditions. Unmodified parental B. anthracis strains did not demonstrate obvious hemolysis under the same conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A spontaneous translational fusion of Bacillus cereus PlcR and PapR activates transcription of PlcR-dependent genes in Bacillus anthracis via binding with a specific palindromic sequence.Infect Immun. 2004 Oct;72(10):5814-23. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5814-5823.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15385482 Free PMC article.
-
The function of PlcR in Bacillus anthracis vaccine strain A16R.Yi Chuan. 2015 May;37(5):494-8. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.15-040. Yi Chuan. 2015. PMID: 25998439
-
PlcR is a pleiotropic regulator of extracellular virulence factor gene expression in Bacillus thuringiensis.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Jun;32(5):1043-53. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01419.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10361306
-
What sets Bacillus anthracis apart from other Bacillus species?Annu Rev Microbiol. 2009;63:451-76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.091208.073255. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19514852 Review.
-
Role of Sphingomyelinase in the Pathogenesis of Bacillus cereus Infection.Biol Pharm Bull. 2020;43(2):250-253. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00762. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020. PMID: 32009113 Review.
Cited by
-
Virulence factor expression patterns in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from infants with cystic fibrosis.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013 Dec;32(12):1583-92. doi: 10.1007/s10096-013-1916-7. Epub 2013 Jul 7. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23832143
-
Characterization of the pathogenicity of a Bacillus cereus isolate from the Mariana Trench.Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):1062-1075. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2088641. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 35733351 Free PMC article.
-
Arcanobacterium haemolyticum Utilizes Both Phospholipase D and Arcanolysin To Mediate Its Uptake into Nonphagocytic Cells.Infect Immun. 2019 Apr 23;87(5):e00832-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00832-18. Print 2019 Mar. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 30745329 Free PMC article.
-
A Bacillus anthracis strain deleted for six proteases serves as an effective host for production of recombinant proteins.Protein Expr Purif. 2011 Nov;80(1):80-90. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2011.05.016. Epub 2011 Aug 7. Protein Expr Purif. 2011. PMID: 21827967 Free PMC article.
-
A computational module assembled from different protease family motifs identifies PI PLC from Bacillus cereus as a putative prolyl peptidase with a serine protease scaffold.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 5;8(8):e70923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070923. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23940667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agaisse, H., M. Gominet, O. A. Okstad, A. B. Kolsto, and D. Lereclus. 1999. PlcR is a pleiotropic regulator of extracellular virulence factor gene expression in Bacillus thuringiensis. Mol. Microbiol. 32:1043-1053. - PubMed
-
- Beecher, D. J., and A. C. Wong. 2000. Cooperative, synergistic and antagonistic haemolytic interactions between haemolysin BL, phosphatidylcholine phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase from Bacillus cereus. Microbiology 146:3033-3039. - PubMed
-
- Briand, J. P., C. Barin, M. H. Van Regenmortel, and S. Muller. 1992. Application and limitations of the multiple antigen peptide (MAP) system in the production and evaluation of anti-peptide and anti-protein antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods. 156:255-265. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

