Differences in host susceptibility to disease progression in the human challenge model of Haemophilus ducreyi infection
- PMID: 14573692
- PMCID: PMC219599
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.11.6658-6663.2003
Differences in host susceptibility to disease progression in the human challenge model of Haemophilus ducreyi infection
Abstract
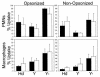
With human volunteers inoculated at two sites with Haemophilus ducreyi, outcomes for a subject were not independent. In a reinfection trial, 2 of 11 previous pustule formers and 6 of 10 previous resolvers resolved all sites of infection. There was no correlation between serum bactericidal or phagocytic activity and outcome in the trial. These data indicate that different hosts are differentially susceptible to disease progression versus resolution in the model.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Human Skin Microbiome Associates with the Outcome of and Is Influenced by Bacterial Infection.mBio. 2015 Sep 15;6(5):e01315-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01315-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26374122 Free PMC article.
-
Serum bactericidal activity and phagocytosis in host defence against Haemophilus ducreyi.Microb Pathog. 1995 Jan;18(1):37-51. Microb Pathog. 1995. PMID: 7783597
-
Dysregulated immune profiles for skin and dendritic cells are associated with increased host susceptibility to Haemophilus ducreyi infection in human volunteers.Infect Immun. 2007 Dec;75(12):5686-97. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00777-07. Epub 2007 Sep 24. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17893130 Free PMC article.
-
Men are more susceptible than women to pustule formation in the experimental model of Haemophilus ducreyi infection.Sex Transm Dis. 2002 Feb;29(2):114-8. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200202000-00009. Sex Transm Dis. 2002. PMID: 11818898
-
Haemophilus ducreyi.Infect Control. 1985 May;6(5):203-5. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700061439. Infect Control. 1985. PMID: 3888902 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of the LspA1 and LspA2 proteins by Haemophilus ducreyi is required for virulence in human volunteers.Infect Immun. 2004 Aug;72(8):4528-33. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.8.4528-4533.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15271912 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking pathways and characterization of CD4 and CD8 cells recruited to the skin of humans experimentally infected with Haemophilus ducreyi.Infect Immun. 2005 Jul;73(7):3896-902. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.7.3896-3902.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15972475 Free PMC article.
-
A Class I Haemophilus ducreyi Strain Containing a Class II hgbA Allele Is Partially Attenuated in Humans: Implications for HgbA Vaccine Efficacy Trials.Infect Immun. 2019 Jun 20;87(7):e00112-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00112-19. Print 2019 Jul. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31036601 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Expression of the Flp proteins by Haemophilus ducreyi is necessary for virulence in human volunteers.BMC Microbiol. 2011 Sep 22;11:208. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-208. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21939541 Free PMC article.
-
Host Polymorphisms in TLR9 and IL10 Are Associated With the Outcomes of Experimental Haemophilus ducreyi Infection in Human Volunteers.J Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 1;214(3):489-95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw164. Epub 2016 Apr 27. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27122592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alhady, S. M. A., and K. Sivanantharajah. 1969. Keloids in various races. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 44:564-566. - PubMed
-
- Al-Tawfiq, J. A., M. E. Bauer, K. R. Fortney, B. P. Katz, A. F. Hood, M. Ketterer, M. A. Apicella, and S. M. Spinola. 2000. A pilus-deficient mutant of Haemophilus ducreyi is virulent in the human model of experimental infection. J. Infect. Dis. 181:1176-1179. - PubMed
-
- Al-Tawfiq, J. A., J. Harezlak, B. P. Katz, and S. M. Spinola. 2000. Cumulative experience with Haemophilus ducreyi in the human model of experimental infection. Sex. Transm. Dis. 27:111-114. - PubMed
-
- Al-Tawfiq, J. A., K. L. Palmer, C.-Y. Chen, J. C. Haley, B. P. Katz, A. F. Hood, and S. M. Spinola. 1999. Experimental infection of human volunteers with Haemophilus ducreyi does not confer protection against subsequent challenge. J. Infect. Dis. 179:1283-1287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

