Self-assembly of single integral membrane proteins into soluble nanoscale phospholipid bilayers
- PMID: 14573860
- PMCID: PMC2366955
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.03267503
Self-assembly of single integral membrane proteins into soluble nanoscale phospholipid bilayers
Abstract
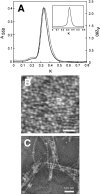
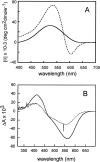
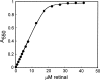
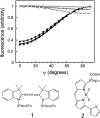
One of the biggest challenges in pharmaceutical research is obtaining integral membrane proteins in a functional, solubilized, and monodisperse state that provides a native-like environment that maintains the spectrum of in vivo activities. Many of these integral membrane proteins are receptors, enzymes, or other macromolecular assemblies that are important drug targets. An example is the general class of proteins composed of seven-transmembrane segments (7-TM) as exemplified by the G-protein-coupled receptors. In this article, we describe a simple system for self-assembling bacteriorhodopsin, as a model protein containing 7-TM helices, with phospholipids to form a nanometer-scale soluble bilayer structure encircled by a 200 amino acid scaffold protein. The result is the single molecule incorporation of an integral membrane protein target into a soluble and monodisperse structure that allows the structural and functional tools of solution biochemistry to be applied.
Figures

References
-
- Atkinson, D., Smith, H.M., Dickson, J., and Austin, J.P. 1976. Interaction of apoprotein from porcine high-density lipoprotein with dimyristoyl lecithin, 1: The structure of the complexes. Eur. J. Biochem. 64 541–547. - PubMed
-
- Bayburt, T.H., Grinkova, Y.V., and Sligar, S.G. 2002. Self-assembly of discoidal phospholipid bilayer nanoparticles with membrane scaffold proteins. Nano Lett. 2 853–856.
-
- Brouillette, C.G., Jones, J.L., Ng, T.C., Kercret, H., Chung, B.H., and Segrest, J.P. 1984. Structural studies of apolipoprotein A-I/phosphatidylcholine recombinants by high-field proton NMR, nondenaturing gradient gel electrophoresis, and electron microscopy. Biochemistry 23 359–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

