Chemical modification of insulin in amyloid fibrils
- PMID: 14573875
- PMCID: PMC2366951
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0360403
Chemical modification of insulin in amyloid fibrils
Abstract
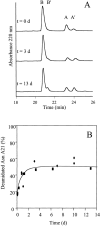
We have investigated the chemical modification of insulin under conditions that promote the conversion of the soluble protein into amyloid fibrils. The modifications that are incorporated into the fibrils include deamidation of Asn A21, Asn B3, and Gln B4. In order to prepare fibrils with minimal deamidation of these residues, the kinetics of aggregation were accelerated by seeding with aliquots of a solution containing preformed fibrils. The resulting fibrils were then reincubated to determine the extent to which chemical modification occurs in the fibril itself. The deamidation of Asn A21 in particular could be followed in detail. Deamidation of this residue in the fibrillar form of insulin was found to occur in only 52 +/- 5% of molecules. This result indicates that there are at least two different packing environments of insulin molecules in the fibrils and suggests that the characterization of chemical modifications may be a useful probe of the environment of polypeptide chains within amyloid fibrils.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The component polypeptide chains of bovine insulin nucleate or inhibit aggregation of the parent protein in a conformation-dependent manner.J Mol Biol. 2006 Jul 7;360(2):497-509. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.05.007. Epub 2006 May 17. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16774767
-
[Investigation of the kinetics of insulin amyloid fibrils formation].Tsitologiia. 2013;55(11):809-14. Tsitologiia. 2013. PMID: 25509136 Russian.
-
Amyloid fibril formation from crude protein mixtures.Biotechnol Prog. 2011 Nov-Dec;27(6):1768-76. doi: 10.1002/btpr.693. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Biotechnol Prog. 2011. PMID: 21910260
-
Insulin structure and stability.Pharm Biotechnol. 1993;5:315-50. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1236-7_11. Pharm Biotechnol. 1993. PMID: 8019699 Review.
-
Structural polymorphism and possible pathways of amyloid fibril formation on the example of insulin protein.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012 Nov;77(11):1237-47. doi: 10.1134/S0006297912110028. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012. PMID: 23240561 Review.
Cited by
-
Perturbation of the stability of amyloid fibrils through alteration of electrostatic interactions.Biophys J. 2011 Jun 8;100(11):2783-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.04.039. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21641324 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of amyloid fibrillation of apo-carbonic anhydrase by flavonoid compounds.J Biosci. 2019 Jun;44(2):46. J Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31180059
-
Photo-activity induced by amyloidogenesis.Protein Sci. 2007 Apr;16(4):561-71. doi: 10.1110/ps.062578307. Epub 2007 Feb 27. Protein Sci. 2007. PMID: 17327395 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of N-Terminally Truncated Derivatives of Insulin Analogs Formed in Pharmaceutical Formulations.Pharm Res. 2018 May 16;35(7):143. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2426-1. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 29770892 Free PMC article.
-
Deamidation accelerates amyloid formation and alters amylin fiber structure.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Aug 1;134(30):12658-67. doi: 10.1021/ja3039486. Epub 2012 Jul 17. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22734583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brange, J., Lngkjaer, L., Havelund, S., and Volund, A. 1992. Chemical stability of insulin. 1. Hydrolytic degradation during storage of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharm. Res. 9 715–727. - PubMed
-
- Brange, J., Andersen, L., Laursen, E.D., Meyn, G., and Rasmussen, E. 1997. Toward understanding insulin fibrillation. J. Pharm. Sci. 86 517–525. - PubMed
-
- Dische, F.E., Wernstedt, C., Westermark, G.T., Westermark, P., Pepys, M.B., Rennie, J.A., Gilbey, S.G., and Watkins, P.J. 1988. Insulin as an amyloid-fibril protein at sites of repeated insulin injections in a diabetic patient. Diabetologia 31 158–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

