Doxycycline is anti-inflammatory and inhibits staphylococcal exotoxin-induced cytokines and chemokines
- PMID: 14576133
- PMCID: PMC253774
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.11.3630-3633.2003
Doxycycline is anti-inflammatory and inhibits staphylococcal exotoxin-induced cytokines and chemokines
Abstract
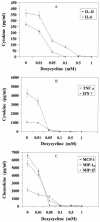
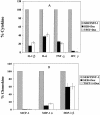
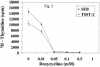
Proinflammatory cytokines mediate the toxic effect of superantigenic staphylococcal exotoxins (SE). Doxycycline inhibited SE-stimulated T-cell proliferation and production of cytokines and chemokines by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. These results suggest that the antibiotic doxycycline has anti-inflammatory effects and is therapeutically useful for mitigating the pathogenic effects of SE.
Figures
References
-
- Baker, M. D., and K. A. Acharya. 2003. Superantigens: structure, function, and diversity, p. 1-31. In T. Krakauer (ed.), Superantigen protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, N.J. - PubMed
-
- Bergdoll, M. S., and P. M. Schlievert. 1984. Toxic shock syndrome toxin. Lancet ii:691.
-
- Boyle, J. R., E. McDermott, M. Crowther, A. D. Wills, P. R. Bell, and M. M. Thompson. 1998. Doxycycline inhibits elastin degradation and reduces metalloproteinase activity in a model of aneurismal disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 27:354-361. - PubMed
-
- Cameron, S. B., M. C. Nawijn, W. W. Kum, H. F. Savelkoul, and A. W. Chow. 2001. Regulation of helper T cell responses to staphylococcal superantigens. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 12:210-222. - PubMed
-
- Chatila, T., and R. S. Geha. 1993. Signal transduction of microbial superantigens via MHC class II molecules. Immunol. Rev. 131:43-59. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

