Synthesis of the Arabidopsis bifunctional lysine-ketoglutarate reductase/saccharopine dehydrogenase enzyme of lysine catabolism is concertedly regulated by metabolic and stress-associated signals
- PMID: 14576281
- PMCID: PMC281635
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.026294
Synthesis of the Arabidopsis bifunctional lysine-ketoglutarate reductase/saccharopine dehydrogenase enzyme of lysine catabolism is concertedly regulated by metabolic and stress-associated signals
Abstract
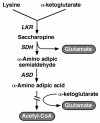
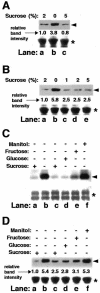
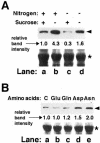
In plants, excess cellular lysine (Lys) is catabolized into glutamic acid and acetyl-coenzyme A; yet, it is still not clear whether this pathway has other functions in addition to balancing Lys levels. To address this issue, we examined the effects of stress-related hormones, abscisic acid (ABA), and jasmonate, as well as various metabolic signals on the production of the mRNA and polypeptide of the bifunctional Lys-ketoglutarate reductase (LKR)/saccharopine dehydrogenase (SDH) enzyme, which contains the first two linked enzymes of Lys catabolism. The level of LKR/SDH was strongly enhanced by ABA, jasmonate, and sugar starvation, whereas excess sugars and nitrogen starvation reduced its level; thus this pathway appears to fulfill multiple functions in stress-related and carbon/nitrogen metabolism. Treatments with combination of hormones and/or metabolites, as well as use of ABA mutants in conjunction with the tester sugars mannose and 3-O-methyl-glucose further supported the idea that the hormonal and metabolic signals apparently operate through different signal transduction cascades. The stimulation of LKR/SDH protein expression by ABA is regulated by a signal transduction cascade that contains the ABI1-1 and ABI2-1 protein phosphatases. By contrast, the stimulation of LKR/SDH protein expression by sugar starvation is regulated by the hexokinase-signaling cascade in a similar manner to the repression of many photosynthetic genes by sugars. These findings suggest a metabolic and mechanistic link between Lys catabolism and photosynthesis-related metabolism in the regulation of carbon/nitrogen partitioning.
Figures







References
-
- Arruda P, Kemper EL, Papes F, Leite A (2000) Regulation of lysine catabolism in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci 5: 324–330 - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254 - PubMed
-
- Deleu C, Coustaut M, Niogert M-F, Larher F (1999) Three new osmotic stress-regulated cDNAs identified by differential display polymerase chain reaction in rapeseed leaf discs. Plant Cell Environ 22: 979–988
-
- Falco SC, Guida T, Locke M, Mauvais J, Sandres C, Ward RT, Webber P (1995) Transgenic canola and soybean seeds with increased lysine. Bio/Technology 13: 577–582 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

