Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 is a survival factor for radiation-exposed intestinal epithelial stem cells in vivo
- PMID: 14576306
- PMCID: PMC275480
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg840
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 is a survival factor for radiation-exposed intestinal epithelial stem cells in vivo
Abstract
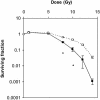
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) is a key enzyme mediating the cellular response to DNA strand breaks. It plays a critical role in genomic stability and survival of proliferating cells in culture undergoing DNA damage. Intestinal epithelium is the most proliferative tissue in the mammalian body and its stem cells show extreme sensitivity to low-level genotoxic stress. We investigated the role of PARP-1 in the in vivo damage response of intestinal stem cells in crypts of PARP-1-/- and control mice following whole-body gamma-irradiation (1 Gy). In the PARP-1-/- mice there was a significant delay during the first 6 h in the transient p53 accumulation in stem cells whereas an increased number of cells were positive for p21(CIP1/WAF1). Either no or only marginal differences were noted in MDM2 expression, apoptosis, induction of or recovery from mitotic blockage, or inhibition of DNA synthesis. We further observed a dose-dependent reduction in crypt survival measured at 4 days post-irradiation in control mice, and this crypt-killing effect was significantly potentiated in PARP-1-/- mice. Our results thus establish that PARP-1 acts as a survival factor for intestinal stem cells in vivo and suggest a functional link with early p53 and p21(CIP1/WAF1) responses.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation is required for p53-dependent signal transduction induced by radiation.Oncogene. 1998 Dec 3;17(22):2819-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202216. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9879988
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 is a positive regulator of the p53-mediated G1 arrest response following ionizing radiation.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 23;278(21):18914-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211641200. Epub 2003 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12642583
-
Combretastatin-A4 prodrug induces mitotic catastrophe in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell line independent of caspase activation and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage.Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Aug;8(8):2735-41. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12171907
-
Cellular responses to DNA damage in the absence of Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Apr 7;245(1):1-10. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8257. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998. PMID: 9535773 Review.
-
Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in cell-cycle checkpoint mechanisms following gamma-irradiation.Biochimie. 1995;77(6):462-5. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(96)88161-2. Biochimie. 1995. PMID: 7578430 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiation damage and radioprotectants: new concepts in the era of molecular medicine.Br J Radiol. 2012 Apr;85(1012):313-30. doi: 10.1259/bjr/16386034. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Br J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22294702 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1 enhances intestinal stem cell survival following radiation injury.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Feb;296(2):G245-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00021.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19056768 Free PMC article.
-
1-(4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl)-4-penylpiperazine increases the number of Peyer's patch-associated regenerating crypts in the small intestines after radiation injury.Radiother Oncol. 2019 Mar;132:8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.11.011. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Radiother Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30825974 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase superfamily in plants.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jan;69(2):175-89. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0793-4. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 21861184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Autoantibodies in Chronic Pulmonary Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 8;21(3):1138. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031138. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32046322 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bürkle A. (2001) Physiology and pathophysiology of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. Bioessays, 23, 795–806. - PubMed
-
- Shall S. and de Murcia,G. (2000) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1: what have we learned from the deficient mouse model? Mutat. Res., 460, 1–15. - PubMed
-
- Muiras M.-L., Müller,M., Schächter,F. and Bürkle,A. (1998) Increased poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity in lymphoblastoid cell lines from centenarians. J. Mol. Med., 76, 346–354. - PubMed
-
- Malanga M., Pleschke,J.M., Kleczkowska,H.E. and Althaus,F.R. (1998) Poly(ADP-ribose) binds to specific domains of p53 and alters its DNA binding functions. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 11839–11843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

