U2AF modulates poly(A) length control by the poly(A)-limiting element
- PMID: 14576315
- PMCID: PMC275465
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg823
U2AF modulates poly(A) length control by the poly(A)-limiting element
Abstract
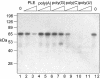
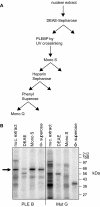
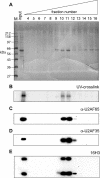
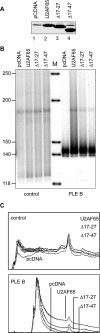
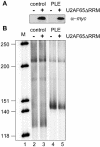
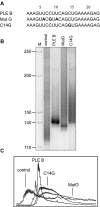
The poly(A)-limiting element (PLE) restricts the length of the poly(A) tail to <20 nt when present in the terminal exon of a pre-mRNA. We previously identified a 65 kDa protein that could be cross-linked to a functional PLE, but not to an inactive mutant element. This binding was competed by poly(U) and poly(C), but not poly(A) or poly(G). Selectivity for the pyrimidine-rich portion of the PLE was demonstrated by RNase footprinting of the binding activity in total nuclear extract. A 65 kDa protein that selectively cross-linked to the functional PLE was purified by conventional chromatography and identified as the large subunit of U2 snRNP auxiliary factor (U2AF). Overexpression of U2AF65 in cells transfected with a PLE-containing reporter construct resulted in the appearance of a population of mRNAs with heterogeneous poly(A) tails. However, this effect was lost following deletion of the C-terminal RNA recognition motifs (RRMs). A C-->G mutation following the AG dinucleotide in the PLE resulted in mRNA with poly(A) ranging from 25-50 nt. This reverted to a discrete, <20 nt poly(A) tail in cells expressing U2AF65. Our results suggest that U2AF modulates the function of the PLE, perhaps by facilitating the binding of another protein to the element.
Figures



Similar articles
-
mRNA with a <20-nt poly(A) tail imparted by the poly(A)-limiting element is translated as efficiently in vivo as long poly(A) mRNA.RNA. 2005 Jul;11(7):1131-40. doi: 10.1261/rna.2470905. Epub 2005 May 31. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15929942 Free PMC article.
-
The poly(A)-limiting element is a conserved cis-acting sequence that regulates poly(A) tail length on nuclear pre-mRNAs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Aug 3;96(16):8943-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.16.8943. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10430875 Free PMC article.
-
The poly(A)-limiting element enhances mRNA accumulation by increasing the efficiency of pre-mRNA 3' processing.RNA. 2005 Jun;11(6):958-65. doi: 10.1261/rna.2020805. Epub 2005 May 4. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15872182 Free PMC article.
-
U2AF homology motifs: protein recognition in the RRM world.Genes Dev. 2004 Jul 1;18(13):1513-26. doi: 10.1101/gad.1206204. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15231733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyadenylation of mRNA precursors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 6;950(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90067-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988. PMID: 2896017 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Differential expression of miRNAs in response to topping in flue-cured tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) roots.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028565. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22194852 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation leukemia virus common integration at the Kis2 locus: simultaneous overexpression of a novel noncoding RNA and of the proximal Phf6 gene.J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(17):11443-56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.11443-11456.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16103195 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA with a <20-nt poly(A) tail imparted by the poly(A)-limiting element is translated as efficiently in vivo as long poly(A) mRNA.RNA. 2005 Jul;11(7):1131-40. doi: 10.1261/rna.2470905. Epub 2005 May 31. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15929942 Free PMC article.
-
A splice site-sensing conformational switch in U2AF2 is modulated by U2AF1 and its recurrent myelodysplasia-associated mutation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 4;48(10):5695-5709. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa293. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32343311 Free PMC article.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nsp9 dimerization is essential for efficient viral growth.J Virol. 2009 Apr;83(7):3007-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01505-08. Epub 2009 Jan 19. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19153232 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

