Expanding the design horizon of antisense oligonucleotides with alpha-L-LNA
- PMID: 14576324
- PMCID: PMC275462
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg820
Expanding the design horizon of antisense oligonucleotides with alpha-L-LNA
Abstract
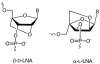
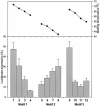
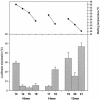
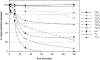
Oligonucleotides containing Locked Nucleic Acids (LNA) to various extents and at various positions were evaluated for antisense activity, RNase H recruitment, nuclease stability and thermal affinity. In this work, two different diastereoisomers of LNA were studied: the beta-D-LNA and the alpha-L-LNA (abbreviated as beta-D-LNA and alpha-L-LNA). Our findings show that the best antisense activity with 16mer gapmers containing beta-D-LNA (oligonucleotides containing consecutive segments of LNA and DNA with a central DNA stretch flanked by two LNA segments, LNA-DNA-LNA) is found with gap sizes between 7 and 10 nt. The optimal gap size is motif-dependent, and requires the right balance between gap size and affinity. Compared to beta-D-LNA, alpha-L-LNA shows superior stability against a 3'-exonuclease. The design possibilities of alpha-L-LNA were explored for different gapmers and other designs, collectively called chimeras. The placement of alpha-L-LNA in the junctions or in the flanks resulted in potent antisense oligonucleotides. Moreover, different chimeras with an alternate composition of DNA, alpha-L-LNA and beta-D-LNA were evaluated in terms of antisense activity and RNase H recruitment. Chimeras with an interrupted DNA stretch with alpha-L-LNA still recruit RNase H and show good levels of antisense activity, while the same design with beta-D-LNA results in a drop in antisense potency. Our findings indicate that alpha-L-LNA is a powerful and versatile nucleotide analogue for designing potent antisense oligonucleotides.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Design of antisense oligonucleotides stabilized by locked nucleic acids.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 May 1;30(9):1911-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.9.1911. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11972327 Free PMC article.
-
Carba-LNA-5MeC/A/G/T modified oligos show nucleobase-specific modulation of 3'-exonuclease activity, thermodynamic stability, RNA selectivity, and RNase H elicitation: synthesis and biochemistry.J Org Chem. 2011 Jun 3;76(11):4408-31. doi: 10.1021/jo200073q. Epub 2011 May 4. J Org Chem. 2011. PMID: 21500818
-
Free-radical ring closure to conformationally locked α-L-carba-LNAs and synthesis of their oligos: nuclease stability, target RNA specificity, and elicitation of RNase H.J Org Chem. 2010 Sep 17;75(18):6122-40. doi: 10.1021/jo100900v. J Org Chem. 2010. PMID: 20738147
-
Locked nucleic acid oligonucleotides: the next generation of antisense agents?BioDrugs. 2007;21(4):235-43. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200721040-00004. BioDrugs. 2007. PMID: 17628121 Review.
-
Locked nucleic acid: a potent nucleic acid analog in therapeutics and biotechnology.Oligonucleotides. 2004;14(2):130-46. doi: 10.1089/1545457041526317. Oligonucleotides. 2004. PMID: 15294076 Review.
Cited by
-
A Kinetic Model Explains Why Shorter and Less Affine Enzyme-recruiting Oligonucleotides Can Be More Potent.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014 Feb 18;3(2):e149. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2013.72. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014. PMID: 24549300 Free PMC article.
-
C5-alkynyl-functionalized α-L-LNA: synthesis, thermal denaturation experiments and enzymatic stability.J Org Chem. 2014 Jun 6;79(11):5062-73. doi: 10.1021/jo5006153. Epub 2014 May 13. J Org Chem. 2014. PMID: 24797769 Free PMC article.
-
Locked nucleic acid: high-affinity targeting of complementary RNA for RNomics.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;173(173):405-22. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27262-3_21. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16594628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Challenges and Strategies of Antisense Oligonucleotide Drug Delivery.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 16;9(4):433. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040433. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33923688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Medicinal Chemistry of Artificial Nucleic Acids and Therapeutic Oligonucleotides.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jul 22;15(8):909. doi: 10.3390/ph15080909. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uhlmann E. and Peyman,A. (1990) Antisense oligonucleotides: A new therapeutic Principle. Chem. Rev., 90, 543–584.
-
- Crooke S.T. (1999) Molecular mechanisms of action of antisense drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1489, 31–44. - PubMed
-
- Cook P.D. (1999) Making drugs out of oligonucleotides: a review and perspective. Nucl. Nucl., 18, 1141–1162. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

