CASP5 target classification
- PMID: 14579323
- PMCID: PMC2656935
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.10555
CASP5 target classification
Abstract
This report summarizes the Critical Assessment of Protein Structure Prediction (CASP5) target proteins, which included 67 experimental models submitted from various structural genomics efforts and independent research groups. Throughout this special issue, CASP5 targets are referred to with the identification numbers T0129-T0195. Several of these targets were excluded from the assessment for various reasons: T0164 and T0166 were cancelled by the organizers; T0131, T0144, T0158, T0163, T0171, T0175, and T0180 were not available in time; T0145 was "natively unfolded"; the T0139 structure became available before the target expired; and T0194 was solved for a different sequence than the one submitted. Table I outlines the sequence and structural information available for CASP5 proteins in the context of existing folds and evolutionary relationships. This information provided the basis for a domain-based classification of the target structures into three assessment categories: comparative modeling (CM), fold recognition (FR), and new fold (NF). The FR category was further subdivided into homologues [FR(H)] and analogs [FR(A)] based on evolutionary considerations, and the overlap between assessment categories was classified as CM/FR(H) and FR(A)/NF. CASP5 domains are illustrated in Figure 1. Examples of nontrivial links between CASP5 target domains and existing structures that support our classifications are provided.
Copyright 2003 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

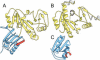
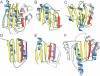
Similar articles
-
Protein structure prediction of CASP5 comparative modeling and fold recognition targets using consensus alignment approach and 3D assessment.Proteins. 2003;53 Suppl 6:410-7. doi: 10.1002/prot.10548. Proteins. 2003. PMID: 14579329
-
CASP5 assessment of fold recognition target predictions.Proteins. 2003;53 Suppl 6:395-409. doi: 10.1002/prot.10557. Proteins. 2003. PMID: 14579328
-
Target domain definition and classification in CASP8.Proteins. 2009;77 Suppl 9(Suppl 9):10-7. doi: 10.1002/prot.22497. Proteins. 2009. PMID: 19603487 Free PMC article.
-
Pretty good guessing: protein structure prediction at CASP5.J Bacteriol. 2003 Jul;185(14):3990-3. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.14.3990-3993.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12837771 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Contemporary approaches to protein structure classification.Bioessays. 1998 Nov;20(11):884-91. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199811)20:11<884::AID-BIES3>3.0.CO;2-H. Bioessays. 1998. PMID: 9872054 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure-based function inference using protein family-specific fingerprints.Protein Sci. 2006 Jun;15(6):1537-43. doi: 10.1110/ps.062189906. Protein Sci. 2006. PMID: 16731985 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing the Role of Conformational Diversity in Protein Structure Prediction.PLoS One. 2016 May 9;11(5):e0154923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154923. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27159429 Free PMC article.
-
MetaMQAP: a meta-server for the quality assessment of protein models.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Sep 29;9:403. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-403. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18823532 Free PMC article.
-
A fold-recognition approach to loop modeling.J Mol Model. 2006 Jan;12(2):125-39. doi: 10.1007/s00894-005-0003-0. Epub 2005 Nov 8. J Mol Model. 2006. PMID: 16096805
-
Identification of family-specific residue packing motifs and their use for structure-based protein function prediction: II. Case studies and applications.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2009 Nov;23(11):785-97. doi: 10.1007/s10822-009-9277-0. Epub 2009 Jun 23. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2009. PMID: 19548090
References
-
- Schlessman JL, Woo D, Joshua-Tor L, Howard JB, Rees DC. Conformational variability in structures of the nitrogenase iron proteins from Azotobacter vinelandii and Clostridium pasteurianum. J Mol Biol. 1998;280:669–685. - PubMed
-
- van den Akker F. Structural insights into the ligand binding domains of membrane bound guanylyl cyclases and natriuretic peptide receptors. J Mol Biol. 2001;311:923–937. - PubMed
-
- Hickman AB, Namboodiri MA, Klein DC, Dyda F. The structural basis of ordered substrate binding by serotonin N-acetyltransferase: enzyme complex at 1.8 A resolution with a bisubstrate analog. Cell. 1999;97:361–369. - PubMed
-
- Angus-Hill ML, Dutnall RN, Tafrov ST, Sternglanz R, Ramakrishnan V. Crystal structure of the histone acetyltransferase Hpa2: a tetrameric member of the Gcn5-related N-acetyltransferase superfamily. J Mol Biol. 1999;294:1311–1325. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

