Neurogenic phenotype of mind bomb mutants leads to severe patterning defects in the zebrafish hindbrain
- PMID: 14579383
- PMCID: PMC2219915
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.10429
Neurogenic phenotype of mind bomb mutants leads to severe patterning defects in the zebrafish hindbrain
Abstract
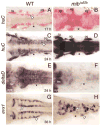
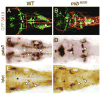
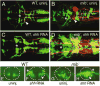
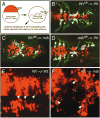
Failure of Notch signaling in zebrafish mind bomb (mib) mutants results in a neurogenic phenotype where an overproduction of early differentiating neurons is accompanied by the loss of later-differentiating cell types. We have characterized in detail the hindbrain phenotype of mib mutants. Hindbrain branchiomotor neurons (BMNs) are reduced in number but not missing in mib mutants. In addition, BMN clusters are frequently fused across the midline in mutants. Mosaic analysis indicates that the BMN patterning and fusion defects in the mib hindbrain arise non-cell autonomously. Ventral midline signaling is defective in the mutant hindbrain, in part due to the differentiation of some midline cells into neural cells. Interestingly, while early hindbrain patterning appears normal in mib mutants, subsequent rhombomere-specific gene expression is completely lost. The defects in ventral midline signaling and rhombomere patterning are accompanied by an apparent loss of neuroepithelial cells in the mutant hindbrain. These observations suggest that, by regulating the differentiation of neuroepithelial cells into neurons, Notch signaling preserves a population of non-neuronal cells that are essential for maintaining patterning mechanisms in the developing neural tube.
Copyright 2003 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Appel B, Korzh V, Glasgow E, Thor S, Edlund T, Dawid IB, Eisen JS. Motoneuron fate specification revealed by patterned LIM homeobox gene expression in embryonic zebrafish. Development. 1995;121:4117–4125. - PubMed
-
- Appel B, Fritz A, Westerfield M, Grunwald DJ, Eisen JS, Riley BB. Delta-mediated specification of midline cell fates in zebrafish embryos. Curr Biol. 1999;9:247–256. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Barth KA, Wilson SW. Expression of zebrafish nk22 is influenced by sonic hedgehog/vertebrate hedgehog-1 and demarcates a zone of neuronal differentiation in the embryonic forebrain. Development. 1995;121:1755–1768. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

