Mixed bilayer containing dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and dipalmitoylphosphatidylserine: lipid complexation, ion binding, and electrostatics
- PMID: 14581212
- PMCID: PMC1303588
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74730-4
Mixed bilayer containing dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and dipalmitoylphosphatidylserine: lipid complexation, ion binding, and electrostatics
Abstract
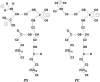
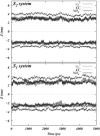
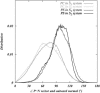
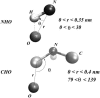
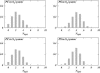
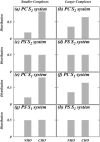
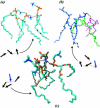
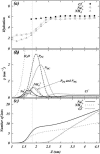
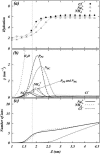
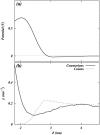
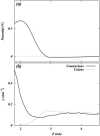
Two mixed bilayers containing dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and dipalmitoylphosphatidylserine at a ratio of 5:1 are simulated in NaCl electrolyte solutions of different concentration using the molecular dynamics technique. Direct NH.O and CH.O hydrogen bonding between lipids was observed to serve as the basis of interlipid complexation. It is deduced from our results and previous studies that dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine alone is less likely to form interlipid complexes than in the presence of bound ions or other bilayer "impurities" such as dipalmitoylphosphatidylserine. The binding of counterions is observed and quantitated. Based upon the calculated ion binding constants, the Gouy-Chapman surface potential (theta) is calculated. In addition we calculated the electrostatic potential profile (Phi) by twice integrating the system charge distribution. A large discrepancy between and the value of Phi at the membrane surface is observed. However, at "larger" distance from the bilayer surface, a qualitative similarity in the z-profiles of Phi and psi(GC) is seen. The discrepancy between the two potential profiles near the bilayer surface is attributed to the discrete and nonbulk-like nature of water in the interfacial region and to the complex geometry of this region.
Figures
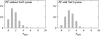
References
-
- Berendsen, H., D. van der Spoel, and R. van Drunen. 1995. GROMACS: a message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comp. Phys. Comm. 91:43–56.
-
- Boda, D., K.-Y. Chan, and D. Henderson. 1998. Monte Carlo simulation of an ion-dipole mixture as a model of an electrical double layer. J. Chem. Phys. 109:7362–7371.
-
- Boda, D., D. Henderson, A. Patrykiejew, and S. Sokolowski. 2000. Simulation and density functional study of simple membrane. II. Solvent effects using the solvent primitive model. J. Chem. Phys. 113:802–806.
-
- Boda, D., D. Henderson, R. Rowley, and S. Sokolowski. 1999. Simulation and density functional study of a simple membrane separating two restricted primitive model electrolytes. J. Chem. Phys. 111:9382–9388.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

