DC-SIGN and L-SIGN can act as attachment receptors for alphaviruses and distinguish between mosquito cell- and mammalian cell-derived viruses
- PMID: 14581539
- PMCID: PMC254289
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.22.12022-12032.2003
DC-SIGN and L-SIGN can act as attachment receptors for alphaviruses and distinguish between mosquito cell- and mammalian cell-derived viruses
Erratum in
- J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(14):7862
Abstract
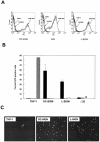
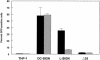
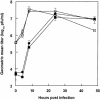
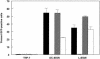
C-type lectins such as DC-SIGN and L-SIGN, which bind mannose-enriched carbohydrate modifications of host and pathogen proteins, have been shown to bind glycoproteins of several viruses and facilitate either cis or trans infection. DC-SIGN and L-SIGN are expressed in several early targets of arbovirus infection, including dendritic cells (DCs) and cells of the reticuloendothelial system. In the present study, we show that DC-SIGN and L-SIGN can function as attachment receptors for Sindbis (SB) virus, an arbovirus of the Alphavirus genus. Human monocytic THP-1 cells stably transfected with DC-SIGN or L-SIGN were permissive for SB virus replication, while untransfected controls were essentially nonpermissive. The majority of control THP-1 cells were permissive when attachment and entry steps were eliminated through electroporation of virus transcripts. Infectivity for the DC-SIGN/L-SIGN-expressing cells was largely blocked by yeast mannan, EDTA, or a DC-SIGN/L-SIGN-specific monoclonal antibody. Infection of primary human DCs by SB virus was also dependent upon SIGN expression by similar criteria. Furthermore, production of virus particles in either C6/36 mosquito cells or CHO mammalian cells under conditions that limited complex carbohydrate content greatly increased SB virus binding to and infection of THP-1 cells expressing these lectins. C6/36-derived virus also was much more infectious for primary human DCs than CHO-derived virus. These results suggest that (i) lectin molecules such as DC-SIGN and L-SIGN may represent common attachment receptor molecules for arthropod-borne viruses, (ii) arbovirus particles produced in and delivered by arthropod vectors may preferentially target vertebrate host cells bearing these or similar lectin molecules, and (iii) a cell line has been identified that can productively replicate alphaviruses but is deficient in attachment receptors.
Figures



References
-
- Bashirova, A. A., T. B. Geijtenbeek, G. C. van Duijnhoven, S. J. Van Vliet, J. B. Eilering, M. P. Martin, L. Wu, T. D. Martin, N. Viebig, P. A. Knolle, V. N. KewalRamani, Y. van Kooyk, and M. Carrington. 2001. A dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN)-related protein is highly expressed on human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and promotes HIV-1 infection. J. Exp. Med. 193:671-678. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernard, K. A., W. B. Klimstra, and R. E. Johnston. 2000. Mutations in the E2 glycoprotein of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus confer heparan sulfate interaction, low morbidity, and rapid clearance from blood of mice. Virology 276:93-103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

