A lymphatic mechanism of rotavirus extraintestinal spread in the neonatal mouse
- PMID: 14581572
- PMCID: PMC254244
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.22.12352-12356.2003
A lymphatic mechanism of rotavirus extraintestinal spread in the neonatal mouse
Abstract
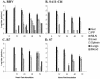
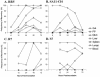
We used the neonatal mouse model of rotavirus infection and virus strains SA11-clone 4 (SA11-Cl4) and Rhesus rotavirus (RRV) to examine the mechanism of the extraintestinal spread of viruses following oral inoculation. The spread-competent viruses, RRV and reassortant R7, demonstrated a temporal progression from the intestine, to the terminal ileum, to the mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), and to the peripheral tissues. SA11-Cl4 was not found outside the intestine. Reassortant virus S7, which was unable to reach the liver in previous studies (E. C. Mossel and R. F. Ramig, J. Virol. 76:6502-6509, 2002), was recovered from 60% of the MLN, suggesting that there are multiple determinants for the spread of virus from the intestine to the MLN. Phenotypic segregation analysis identified RRV genome segment 6 (VP6) as a secondary determinant of the spread of virus to the MLN (P = 0.02) in reassortant viruses containing segment 7 from the spread-incompetent parent. These data suggest that in the orally infected neonatal mouse, the extraintestinal spread of rotavirus occurs via a lymphatic pathway, and the spread phenotype is primarily determined by NSP3 and can be modified by VP6.
Figures
References
-
- Blutt, S. E., C. D. Kirkwood, V. Parreno, K. L. Warfield, M. Ciarlet, M. K. Estes, K. Bok, R. F. Bishop, and M. E. Conner. Rotavirus antigenemia/viremia: a common event? Lancet, in press. - PubMed
-
- Brown, K. A., and P. A. Offit. 1998. Rotavirus-specific proteins are detected in murine macrophages in both intestinal and extraintestinal lymphoid tissues. Microb. Pathog. 24:327-331. - PubMed
-
- Contino, M. F., T. Lebby, and E. L. Arcinue. 1994. Rotaviral gastrointestinal infection causing afebrile seizures in infancy and childhood. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 12:94-95. - PubMed
-
- Estes, M. K. 2001. Rotaviruses and their replication, p. 1747-1785. In D. M. Knipe and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields virology, 4th ed. Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, Pa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

