Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain
- PMID: 14581618
- PMCID: PMC263865
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2234031100
Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain
Abstract
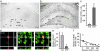
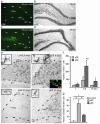
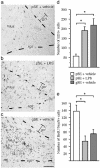
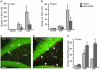
New hippocampal neurons are continuously generated in the adult brain. Here, we demonstrate that lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation, which gives rise to microglia activation in the area where the new neurons are born, strongly impairs basal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. The increased neurogenesis triggered by a brain insult is also attenuated if it is associated with microglia activation caused by tissue damage or lipopolysaccharide infusion. The impaired neurogenesis in inflammation is restored by systemic administration of minocycline, which inhibits microglia activation. Our data raise the possibility that suppression of hippocampal neurogenesis by activated microglia contributes to cognitive dysfunction in aging, dementia, epilepsy, and other conditions leading to brain inflammation.
Figures
References
-
- Cameron, H. A. & McKay, R. D. (2001) J. Comp. Neurol. 435, 406-417. - PubMed
-
- Shors, T. J., Miesegaes, G., Beylin, A., Zhao, M., Rydel, T. & Gould, E. (2001) Nature 410, 372-376. - PubMed
-
- Santarelli, L., Saxe, M., Gross, C., Surget, A., Battaglia, F., Dulawa, S., Weisstaub, N., Lee, J., Duman, R., Arancio, O., Belzung, C. & Hen, R. (2003) Science 301, 805-809. - PubMed
-
- Zitnik, G. & Martin, G. M. (2002) J. Neurosci. Res. 70, 258-263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

