A dominant negative mutant of TLK1 causes chromosome missegregation and aneuploidy in normal breast epithelial cells
- PMID: 14583098
- PMCID: PMC270066
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-4-16
A dominant negative mutant of TLK1 causes chromosome missegregation and aneuploidy in normal breast epithelial cells
Abstract
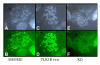
Background: In Arabidopsis thaliana, the gene Tousled encodes a protein kinase of unknown function, but mutations in the gene lead to flowering and leaf morphology defects. We have recently cloned a mammalian Tousled-Like Kinase (TLK1B) and found that it phosphorylates specifically histone H3, in vitro and in vivo. We now report the effects that overexpression of a kinase-dead mutant of TLK1B mediates in a normal diploid cell line.
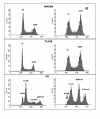
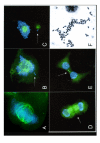
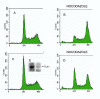
Results: Expression of a kinase-dead mutant resulted in reduction of phosphorylated histone H3, which could have consequences in mitotic segregation of chromosomes. When analyzed by FACS and microscopy, these cells displayed high chromosome number instability and aneuploidy. This phenomenon was accompanied by less condensed chromosomes at mitosis; failure of a number of chromosomes to align properly on the metaphase plate; failure of some chromosomes to attach to microtubules; and the occasional presentation of two bipolar spindles. We also used a different method (siRNA) to reduce the level of endogenous TLK1, but in this case, the main result was a strong block of cell cycle progression suggesting that TLK1 may also play a role in progression from G1. This block in S phase progression could also offer a different explanation of some of the later mitotic defects.
Conclusions: TLK1 has a function important for proper chromosome segregation and maintenance of diploid cells at mitosis in mammalian cells that could be mediated by reduced phosphorylation of histone H3 and condensation of chromosomes, although other explanations to the phenotype are possible.
Figures


References
-
- Schmiesing JA, Gregson HC, Zhou S, Yokomori K. A human condensing complex containing hCAP-C-hCAP-E and CNAP1, a homolog of Xenopus XCAP-D2, colocalizes with phosphorylated histone H3 during early stage of mitotic chromosome condensation. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:6996–7006. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.18.6996-7006.2000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

