Extracapsular dissection for clinically benign parotid lumps: reduced morbidity without oncological compromise
- PMID: 14583757
- PMCID: PMC2394403
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601281
Extracapsular dissection for clinically benign parotid lumps: reduced morbidity without oncological compromise
Abstract
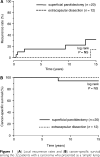
Previous studies have shown that extracapsular dissection (ECD) is an alternative approach to superficial parotidectomy (SP) for pleomorphic adenoma parotid tumours, associated with low recurrence rates equal to those following SP, but with significantly reduced morbidity. However, if a malignant tumour masquerades as a clinically benign lump, this approach may be inappropriate. This study addressed this question by analysing the outcome of 821 consecutive patients with parotid tumours treated at one centre over 40 years and with a median 12 (range 5-30) years follow-up. Tumours were classified as 'simple' (discrete, mobile, < 4 cm: n=662) and 'complex' (deep, fixed, facial nerve palsy, > or =4 cm: n=159). Among the 'simple' or clinically benign tumours, 503 patients underwent ECD; 159 patients underwent SP. In all, 32 (5%) clinically benign cases were subsequently revealed as malignant histologies (ECD, 12; SP, 20). For each group, 5- and 10-year cancer-specific survival rates were 100 and 98%, respectively. There were no differences in recurrence rates when subanalysed by surgical groups, but ECD was associated with significantly reduced morbidity (P < 0.001). This study demonstrates that ECD is a viable alternative to superficial parotidectomy for the majority of parotid tumours, associated with reduced morbidity without oncological compromise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Extracapsular dissection versus superficial parotidectomy for treatment of parotid benign tumors: evidence based medicine analysis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Jun 5;31(11):863-869. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2017.11.011. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29775003 Chinese.
-
Extracapsular dissection with a transparotid facial nerve dissection approach versus partial superficial parotidectomy for benign tumours in the tail of the parotid gland: a single-centre retrospective study of 89 patients.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023 Jun;52(6):656-662. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2022.09.003. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023. PMID: 36127208
-
Surgical management of epithelial parotid tumours.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2004 Jul;14(7):394-9. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2004. PMID: 15279739
-
The significance of the margin in parotid surgery for pleomorphic adenoma.Laryngoscope. 2002 Dec;112(12):2141-54. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200212000-00004. Laryngoscope. 2002. PMID: 12461331
-
Contemporary management of benign parotid tumours - the increasing evidence for extracapsular dissection.Oral Dis. 2017 Jan;23(1):18-21. doi: 10.1111/odi.12518. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Oral Dis. 2017. PMID: 27260128 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of surgical techniques and guide for decision making in the treatment of benign parotid tumors.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Jan;278(1):15-29. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06250-x. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 32749609 Review.
-
Preoperative diagnostic of parotid gland neoplasms: fine-needle aspiration cytology or core needle biopsy?Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Nov;275(11):2609-2613. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5131-0. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 30238310
-
Patient-Reported Quality-of-Life Outcome Measure After Parotidectomy.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 May 1;151(5):441-449. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2024.5253. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 40178828
-
Functional gland-preserving surgery for submandibular gland pleomorphic adenoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022 Oct;148(10):2623-2629. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03844-8. Epub 2021 Oct 27. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34705103 Free PMC article.
-
Benign tumours affecting the deep lobe of the parotid gland: how to select the optimal surgical approach.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2015 Apr;35(2):80-7. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2015. PMID: 26019390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson R (1975) Benign mixed tumours of the parotid gland. In Cancer of the Head and Neck, Proceedings of an International Symposium, Chamvers RG, Janssen de Limpens AMP, Jaques DA, Routledge RT (eds) Vol 37, pp 1555–1558. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica
-
- Frankenthaler RA, Luna MA, Lee SS, Ang KK, Byers RM, Guillamondegui OM, Wolf P, Goepfert H (1991) Prognostic variables in parotid gland cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 117: 1251–1256 - PubMed
-
- Gleave EN (1995) An alternative to superficial parotidectomy: extracapsular dissection. In Colour Atlas and Text of Salivary Glands: Diseases, Disorders and Surgery, de Burgh Norman J, McGurk M (eds) pp 165–172. London: Mosby-Wolf
-
- Gleave EN, Whittaker JS, Nicholson A (1979) Salivary tumours–experience over thirty years. Clin Otolaryngol 4: 247–257 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources