Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogues for endometriosis: bone mineral density
- PMID: 14583930
- PMCID: PMC7027701
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001297
Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogues for endometriosis: bone mineral density
Abstract
Background: Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogues (GnRHas) are generally well tolerated, and are effective in relieving the symptoms of endometriosis (Prentice 2003). Unfortunately the low oestrogen state that they induce is associated with adverse effects including an acceleration in bone mineral density (BMD) loss.
Objectives: To determine the effect of treatment with gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogues (GnRHas) on the bone mineral density of women with endometriosis, compared to placebo, no treatment, or other treatments for endometriosis, including GnRHas with add-back therapy.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Menstrual Disorders and Subfertility Group's specialised register of controlled trials (23rd October 2002) and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (Cochrane Library, issue 4, 2002). We also carried out electronic searches of MEDLINE (1966 - March Week 2 2003) and EMBASE (1980 - March Week 2 2003). We also searched the reference lists of articles and contacted researchers in the field.
Selection criteria: Prospective, randomised controlled studies of the use of GnRHas for the treatment of women with endometriosis were considered, where bone density measurements were an end point. The control arm of the studies was either placebo, no treatment, another medical therapy for endometriosis, or GnRHas with add-back therapy.
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewers (JF and MS) independently assessed trial quality and extracted data. Study authors were contacted for additional information.
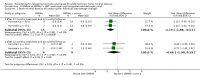
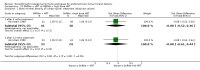
Main results: Thirty studies involving 2,391 women were included, however only 15, involving 910 women, could be included in the meta-analysis. The meta-analysis showed that danazol and progesterone + oestrogen add-back are protective of BMD at the lumbar spine both during treatment and for up to six and twelve months after treatment, respectively. Between the groups receiving GnRHa and the groups receiving danazol/gestrinone, there was a significant difference in percentage change of BMD after six months of treatment, the GnRH analogue producing a reduction in BMD from baseline and danazol producing an increase in BMD (SMD -3.43, 95 % CI -3.91 to -2.95). Progesterone only add-back is not protective; after six months of treatment absolute value BMD measurements of the lumbar spine did not differ significantly from the group receiving GnRH analogues (SMD 0.15, 95 % CI -0.21 to 0.52). In the comparison of GnRHa versus GnRHa + HRT add-back, that is oestrogen + progesterone or oestrogen only, there was a significantly bigger BMD loss in the GnRHa only group (SMD -0.49, 95 % CI -0.77 to -0.21). These numbers reflect the absolute value measurements at the lumbar spine after six months of treatment. Due to the small number of studies in the comparison we are unable to conclude whether calcium-regulating agents are protective. No difference was found between low and high dose add-back regimes but again only one study was identified for this comparison. Only one study comparing GnRH analogues with placebo was identified, but the study gave no data. No studies comparing GnRH with the oral contraceptive pill (OCP) or progestagens were identified.
Reviewer's conclusions: Both danazol and progesterone + oestrogen add-back have been shown to be protective of BMD, while on treatment and up to six and 12 months later, respectively. However, by 24 months of follow-up there was no difference in BMD in those women who had HRT add-back. Studies of danazol versus GnRHa did not report long-term follow-up. The significant side effects associated with danazol limit its use.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures

















References
References to studies included in this review
Aisaka 2000 {published data only}
-
- Aisaka K, Nakagawa K, Uesato T, Miwa A, Koshino T, Ooka F, et al. Effectiveness of long term GnRH agonist administration for treatment of endometriosis combined with oestrogen‐progestogen add back therapy. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 2000. [MDSG # 6384]
Chan 1993 {published data only}
-
- Chan CLK, Soon SB, Loh FH, Devendra S, Ng SC, Ratnam SS. Comparitive study of gestrinone, danazol and decapeptyl CR in the treatment of endometriosis. 2nd International Scientific Meeting of the Royal College of Obstetricians , Hong Kong. 1993:82. [MDSG # 1413]
Crosignani 1996 {published data only}
-
- Crosignani PG, Cecco L, Gastaldi A, Venturini PL, Oldani S, Vegetti W, et al. Leuprolide in a 3‐monthly versus a monthly depot formulation for the treatment of symptomatic endometriosis: a pilot study. Human Reproduction 1996;11(12):2732‐5. - PubMed
Dawood 1995 {published data only}
-
- Dawood MY, Ramos J, Khan‐Dawood FS. Depot leuprolide acetate versus danazol for the treatment of pelvic endometriosis: changes in vertebral bone mass and serum estrodiol and calcitonin. Fertility and Sterility 1995;63(6):1177‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dodin 1991 {published data only}
-
- Dodin S, Lemay A, Maheux R, Dumont M, Turcot‐Lemay L. Bone mass in endometriosis patients treated with GnRH agonist implant or danazol. Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1991;77(3):410‐5. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 186] - PubMed
Edmonds 1994 {published data only}
-
- Edmonds DK, Howell R. Can hormone replacement therapy be used during medical therapy of endometriosis?. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1994;101(supplement 10):24‐6. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 816] - PubMed
Eldred 1992 {published data only}
-
- Eldred JM, Haynes PJ, Thomas EJ. A randomized double blind placebo controlled trial of the effects on bone metabolism of the combination of nafarelin acetate and norethisterone. Clincal Endocrinology 1992;37:354‐9. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 272] - PubMed
Franke 2000 {published data only}
-
- Franke H, Enschede K, Weijer P, Pennings T, Mooren M. Gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone agonist plus add‐back for the treatment of endometriosis. A prospective, randomized, placebo controlled, double blind trial. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 2000. [MDSG # 6383] - PubMed
-
- Franke HR, Weijer PHM, Pennings TMM, Mooren MJ. Gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone agonist plus 'add‐back' hormone replacement therapy for treatment of endometriosis: a prospective, randomized, placebo‐controlled, double blind trial. Fertility and Sterility 2000;74(3):534‐9. [MDSG # 3751] - PubMed
Fukushima 1993 {published data only}
-
- Fukushima M. Changes in bone mineral content following hormone treatment for endometriosis. International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics 1995;50(supplement 1):S17‐S21. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 482] - PubMed
-
- Fukushima M, Shindo M, Sato K. Hormone treatment related bone mineral content changes in Japanese women with endometriosis. Asia‐Oceania Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1993;19(3):299‐307. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 679] - PubMed
Gnoth 1999 {published data only}
-
- Freundl G, Gödtke K, Gnoth Ch, Godehardt E, Kienle E. Steroidal 'add‐back' therapy in patients treated with GnRH agonists. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 1998;45(supplement 1):22‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gnoth C, Godtke K, Freundl G, Godehardt E, Kienle E. Effects of add‐back therapy on bone mineral density and pyridinium crosslinks in patients with endometriosis treated with gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone agonists. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 1999;1(47):37‐41. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 5932] - PubMed
-
- Gödtke K, Freudl G, Gnoth Ch. Effects of the add‐back therapy on bone mineral density and pyridinium‐crosslinks under central suppression by GnRH‐agonists. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1997;76 Suppl(1):32.
Gregoriou 1997 {published data only}
-
- Gregoriou O, Konidaris S, Vitoratos N, Papadias C, Paoulias I, Chryssicopoulos A. Gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone analogue plus hormone replacement therapy for the treatment of endometriosis: a randomised controlled trial. International Journal of Fertility 1997;42(6):406‐11. [MDSG # 4160] - PubMed
Henzl 1990 {published data only}
-
- Henzl MR, Monroe SE. Nafarelin: a new medical therapy for endometriosis. Progress in Clinical and Biological Research 1990;323:343‐55. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 438] - PubMed
-
- Henzl R, Kwei L. Efficacy and safety of nafarelin in the treatment of endometriosis. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1990;162(Number 2):570‐4. [MEDLINE: ; Cochrane MDSG # 436] - PubMed
Henzl 1990 study 1 {published data only}
-
- Henzl MR, Kwei L. Efficacy and safety of nafarelin in the treatment of endometriosis. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1990;162(2):570‐4. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 436] - PubMed
-
- Henzl MR, Monroe SE. Nafarelin: A new medical therapy for endometriosis. Progress in Clinical & Biological Research 1990;323:343‐55. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 438] - PubMed
Henzl 1990 study 2 {published data only}
-
- Henzl MR, Kwei L. Efficacy and safety of nafarelin in the treatment of endometriosis. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1990;162(2):570‐574. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 436] - PubMed
-
- Henzl MR, Monroe SE. Nafarelin: A new medical therapy for endometriosis. Progress in Clinical & Biological Research 1990;323:343‐355. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 438] - PubMed
Hornstein 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Wesberg GW, Casino LA. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add‐back in endometriosis: a 12‐month study. Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1998;91(1):16‐24. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 3179] - PubMed
-
- Surrey ES, Hornstein MD. [Prolonged GnRH agonist and add‐back therapy for symptomatic endometriosis patients: long term follow up of a 12 month clinical trial]. Abstracts from ASRM/CFAS Conjoint Annual Meeting. Toronto, Canada, 1999; Vol. 72, issue 3, supplement 1:80. [MDSG # 5633]
-
- Surrey ES, Hornstein MD. Prolonged GnRH agonist and add‐back therapy for symptomatic endometriosis: long‐term follow‐up. Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2002;99(5 part 1):709‐719. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 7355] - PubMed
Hornstein p + hd o {published data only}
-
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, Casino LA. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add‐back in endometriosis: a 12‐month study. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1998;91(1):16‐24. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 3179] - PubMed
-
- Surrey ES, Hornstein MD. Prolonged GnRH agonist and add‐back therapy for symptomatic endometriosis patients: long term follow‐up of a 12 month clinical trial. Abstracts from ASRM/CFAS Conjoint Annual Meeting. Toronto, Canada, 1999; Vol. 72, issue 3, supplement 1:80. [MDSG # 5633]
-
- Surrey ES, Hornstein MD. Prolonged GnRH agonist and add‐back therapy for symptomatic endometriosis: long‐term follow‐up. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2002;99(5 part 1):709‐19. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 7355] - PubMed
Hornstein p + ld o {published data only}
-
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, Casino LA. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add‐back in endometriosis: a 12‐month atudy. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1998;91(1):16‐24. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 3179] - PubMed
-
- Surrey ES, Hornstein MD. Prolonged GnRH agonist and add‐back therapy for symptomatic endometriosis patients: long term follow‐up of a 12 month cinical trial. Abstracts from ASRM/CFAS Conjoint Annual Meeting. Toronto, Canada, 1999; Vol. 72, issue 3 suppl 1:80. [MDSG # 5633]
-
- Surrey ES, Hornstein MD. Prolonged GnRH agonist and add‐back therapy for symptomatic endometriosis: long‐term follow‐up. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2002;99(5 part 1):709‐19. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 7355] - PubMed
Hornstein prog only {published data only}
-
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, Casino LA. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add‐back in endometriosis: a 12‐month study. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1998;91(1):16‐24. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 3179] - PubMed
-
- Surrey ES, Hornstein MD. Prolonged GnRH agonist and add‐back therapy for symptomatic endometriosis patients: long term follow‐up of a 12 month clinical trial. Abstracts from ASRM/CFAS Conjoint Annual Meeting. 1999; Vol. 72, issue 3 suppl 1:80. [MDSG # 5633]
-
- Surrey ES, Hornstein MD. Prolonged GnRH agonist and add‐back therapy for symptomatic endometriosis: long‐term follow‐up. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2002;99(5 part 1):709‐19. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 7355] - PubMed
Howell 1995 {published data only}
-
- Howell R, Edmonds D, Dowsett M, Crook D, Lees B, Stevenson JC. Gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone analogue (goserelin) plus hormone replacement therapy for the treatment of endometriosis:a randomised controlled trial. Fertility and Sterility 1995;64(3):474‐81. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 202] - PubMed
Irahara 2000 {published data only}
-
- Irahara M, Uemura H, Yasui T, Kinoshita K, Yamada M, Tezuka M, et al. Efficacy of every‐other‐day administration of conjugated equine estrogen and medroxyprogesterone acetate on gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone agonists treatment in women with endometriosis. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 2001;52:217‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kiesel 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kiesel L, Schweppe KW, Sillem M, Siebzehnrubl E. Should add‐back therapy for endometriosis be deferred for optimal results?. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1996;103(suppl 14):15‐7. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 2030] - PubMed
Lindsay 1996 {published data only}
-
- Lindsay PC, Shaw RW, Bennink HJ, Kicovic P. The effect of add‐back treatment with tibolone (livial) on patients treated with the gonadotrophin releasing hormone agonist triptorelin (decapeptyl). Fertility and Sterility 1996;65(2):342‐47. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 1288] - PubMed
Miller 1990 {published data only}
-
- Miller JD. Leuprolide Acetate for the Treatment of Endometriosis. Progress in Clinical and Biological Research 1990;323:337‐41. [MDSG # 455] - PubMed
-
- Wheeler JM, Knittle JD, Miller JD. Depot leuprolide acetate versus danazol in the treatment of women with symptomatic endometriosis: A multicenter, double‐blind randomized clinical trial II. Assessment of safety. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1993;169(1):26‐35. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler JM, Knittle JD, Miller JD. Depot leuprolide versus danazol in treatment of women with symptomatic endometriosis I. Efficacy results. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1992;167(5):1367‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Miller 1990 study 1 {published data only}
-
- Miller JD. Leuprolide acetate for the treatment of endometriosis. Progress in Clinical & Biological Research 1990;323:337‐41. [MDSG # 455] - PubMed
-
- Wheeler JM, Knittle JD, Miller JD. Depot leuprolide acetate versus danazol in the treatment of women with symptomatic endometriosis: A multicenter, double‐blind randomized clinical trial II. Assessment of safety. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1993;169(1):26‐35. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler JM, Knittle JD, Miller JD. Depot leuprolide versus danazol in treatment of women with symptomatic endometriosis I. Efficacy results. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1992;167(5):1367‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Miller 90 study2 DPA {published data only}
-
- Miller JD. Leuprolide acetate for the treatment of endometriosis. Progress in Clinical & Biological Research 1990;323:337‐41. [MDSG # 455] - PubMed
-
- Wheeler JM, Knittle JD, Miller JD. Depot leuprolide acetate versus danazol in the treatment of women with symptomatic endometriosis: A multicenter, double‐blind randomized clinical trial II. Assessment of safety. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1993;169(1):26‐35. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler JM, Knittle JD, Miller JD. Depot leuprolide versus danazol in treatment of women with symptomatic endometrisosis I. Efficacy results. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1992;167(5):1367‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Miller 90 Study2 QCT {published data only}
-
- Miller JD. Leuprolide acetate for the treatment of endometriosis. Progress in Clinical & Biological Research 1990;323:337‐41. [MDSG # 455] - PubMed
-
- Wheeler JM, Knittle JD, Miller JD. Depot leuprolide acetate versus danazol in the treatment of women with symptomatic endometriosis: A multicenter, double‐blind randomized clinical trial II. Assessment of safety. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1993;169(1):26‐35. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler JM, Knittle JD, Miller JD. Depot leuprolide versus danazol in treatment of women with symptomatic endometriosis I. Efficacy results. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1992;167(5):1367‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moghissi 1996 {published data only}
-
- Moghissi KS. Add‐back therapy in the treatment of endometriosis: The North American Experience. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1996;103(suppl 14):14. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 1863] - PubMed
-
- Moghissi KS, Schlaff WD, Olive DL, Skinner MA, Yin H. Goserelin acetate (zoladex) with or without hormone replacement therapy for the treatment of endometriosis. Fertility and Sterility 1998;69(6):1056‐62. [MDSG # 4514] - PubMed
Mukherjee 1996 {published data only}
-
- Mukherjee T, Barad D, Turk R, Freeman R. A randomized, placebo‐controlled study on the effect of cyclic intermittent etidronate therapy on the bone mineral density changes associated with six months of gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist treatment. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1996;175:105‐9. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 1738] - PubMed
Rock 1993 {published data only}
-
- Rock JA, Truglia JA, Caplan RJ, The Zoladex Endometriosis Study Group. Zoladex (goserelin acetate implant) in the treatment of endometriosis: a randomized comparison with danazol. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1993;82(2):198‐205. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Roux 1995 {published data only}
-
- Borderie D, Cherruau B, Dougados M, Ekindijan OG, Roux C. Biochemical markers as predictors of bone mineral density changes after GnRH agonist treatment. Calcified Tissue International 1998;62:21‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Roux C, Pelissier C, Listrat V, Kolta S, Simonetta C, Guingard M, et al. Bone loss during gonadotrophin releasing hormone agonist treatment and the use of nasal calcitonin. Osteoporosis International 1995;5(3):185‐90. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 724] - PubMed
Roux 1995 100 IU {published data only}
-
- Borderie D, Cherruau B, Dougados M, Ekindijan OG, Roux C. Biochemical markers as predictors of bone mineral density changes after GnRH agonist treatment. Calcified Tissue International 1998;62:21‐5. - PubMed
-
- Roux C, Pelissier C, Listrat V, Kolta S, Simonetta C, Guignard M, et al. Bone loss during gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist treatment and use of nasal calcitonin. Osteoporosis International 1995;5:185‐90. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 724] - PubMed
Roux 1995 200 IU {published data only}
-
- Borderie D, Cherruau B, Dougados M, Ekindijan OG, Roux C. Biochemical markers as predictors of bone mineral density changes after GnRH agonist treatment. Calcified Tissue International 1998;62:21‐5. - PubMed
-
- Roux C, Pelissier C, Listrat V, Kolta S, Simonetta C, Guignard M, et al. Bone loss during gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist treatment and use of nasal calcitonin. Osteoporosis International 1995;5:185‐90. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 724] - PubMed
Sillem 1999 {published data only}
-
- Seibel MJ, Woitge HW, Parviz M, Sillem M, Kiesel L, Pfeilschifter J, et al. Medrogestone prevents accelerated bone turnover in GnRH analogue treated endometriosis. Klinisches Labor. 1996; Vol. 42, issue 12:1075‐78. [MDSG # 1913]
-
- Sillem M, Parviz M, Woitge HW, Kiesel L, Ulrich U, Holst Th, et al. Add‐back medrogestone does not prevent bone loss in premenopausal women treated with goserelin. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology and Diabetes 1999;107:379‐85. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Somekawa +vitK +vitD {published data only}
-
- Somekawa Y, Chigughi M, Harada M, Ishibashi T. Use of vitamin K2 (menatetrenone) and 1,25‐dihydroxyvitamin D3 in the prevention of bone loss induced by leuprolide. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 1999;84(8):2700‐04. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Somekawa 1999 {published data only}
-
- Somekawa Y, Chigughi M, Harada M, Ishibashi T. Use of vitamin K² (menatetrenone) and 1,25 ‐ dihydroxyvitamin D³ in the prevention of bone loss induced by leuprolide. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1999;84(8):2700‐04. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Somekawa 1999 + vitD {published data only}
-
- Somekawa Y, Chigughi M, Harada M, Ishibashi T. Use of vitamin K2 (menatetrenone) and 1,25‐dihydroxyvitamin D3 in the prevention of bone loss induced by leuprolide. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 1999;84(8):2700‐04. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Somekawa 1999 + vitK {published data only}
-
- Somekawa Y, Chigughi M, Harada M, Ishibashi T. Use of vitamin K2 (menatetrenone) and 1,25‐dihydroxyvitamin D3 in the prevention of bone loss induced by leuprolide. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 1999;84(8):2700‐04. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Surrey 1992 {published data only}
-
- Surrey ES, Judd HL. Reduction of vasomotor symptoms and bone mineral density loss with combined norethidrone and long‐acting gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone agonist therapy of symptomatic endometriosis: a prospective randomised trial. Journal of Clincal Endocrinology and Metabolism 1992;75(2):558‐63. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 274] - PubMed
Vella 1995 {published data only}
-
- Vella A, Brincat M, Galea R, Muscat Baron Y. Skin thickness and bone density: effect of add‐back therapy in women on GnRH analogues. 27th British Congress of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, Dublin. 1995:155. [MDSG # 221]
Vercillini 1996 {published data only}
-
- The Gestrinone Italian Study Group. Gestrinone versus a gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone agonist for the treatment of pelvic pain associated with endometriosis: a multicentre, randomized, double blind study. Fertility and Sterility 1996;66(6):911‐19. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 1755] - PubMed
Whitehouse 1990 {published data only}
-
- Whitehouse RW, Adams JE, Bancroft K, Vaughan‐Williams CA, Elstein M. The effects of nafarelin and danazol on vertebral trabecular bone mass in patients with endometriosis. Clinical Endocrinology 1990;3(33):365‐73. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 130] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agarwal 1997 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal SK, Hamrang C, Henzl MR, Judd HL. Nafarelin vs. leuprolide acetate depot for endometriosis. Changes in bone mineral density and vasomotor symptoms. Journal of Reproductive Medicine for the Obstetrician and Gynecologist 1997;42(7):413‐23. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 3178] - PubMed
Agarwal 1999 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal SK. The impact of 6 months GnRH agonist therapy for the treatment of endometriosis on bone mineral density: is there an age‐related effect?. Abstracts of the 15th Annual Meeting of the ESHRE, France. Tours, France, 1999; Vol. 14, issue 1:260. [MDSG # 5147]
Chang 1996 {published data only}
-
- Chang SP, Ng H‐T. A randomised comparative study of the effect of leuprorelin acetate depot and danazol in the treatment of endometriosis. Chinese Medical Journal (Taipei) 1996;57(6):431‐37. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cirkel 1995 {published data only}
-
- Cirkel U, Ochs H, Schneider HPG. A randomized, comparative trial of triptorelin depot (D‐Trp6‐LHRH) and danazol in the treatment of endometriosis. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 1995;59:61‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Cirkel U, Ochs H, Schneider HPG. GNRH analogue depot versus danazol in the treatment of endometriosis. 3rd International Symposium on Gynaecological Endocrinology. Geneva, Switzerland, 1993:20. [MDSG # 1899]
Claesson 1989 {published data only}
-
- Claesson B, Berquist C. Clinical experience treating endometriosis with nafarelin. The Journal of Reproductive Medicine 1989;34(12 suppl):1025‐28. [MDSG # 177] - PubMed
Dawood 1989 {published data only}
-
- Dawood MY, Lewis V, Ramos J. Cortical and trabecular bone mineral content in women with endometriosis: effect of gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist and danazol. Fertility and Sterility 1989;52(1):21‐6. [MDSG # 504] - PubMed
Dawood 1997 {published data only}
-
- Dawood MY, Obasiolu CW, Ramos J, Khan‐Dawood FS. Clinical, endocrine and metabolic effects of two doses of gestrinone in treatment of pelvic endometriosis. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1997;176(2):387‐94. [MDSG # 3703] - PubMed
Finkelstein 1994 {published data only}
-
- Finkelstein J.S, Klibanski A, Shaefer E. H, Hornstein M.D, Schiff I, Neer R.M. Parathyroid hormone for the prevention of bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency. The New England Journal of Medicine 1994;331(24):1618‐22. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 281] - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein JS, Arnold AL. Increases in bone mineral density after discontinuation of daily parathyroid hormone and gonadotrophin‐releasing analog administration in women with endometriosis.. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1999;84(4):1214‐19. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein JS, Kibanski A, Arnold AL, Toth TL, Hornstein MD, Neer RM. Prevention of estrogen deficiency‐related bone loss with human parathyroid hormone. JAMA 1998;280(12):1067‐73. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fogelman 1994 {published data only}
-
- Fogelman I, Fentiman I, Hamed H, Studd JWW, Leather AT. Goserelin (zoladex) and the skeleton. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1994;101(Suppl 10):19‐23. - PubMed
Giorgino 1991 {published data only}
-
- Giorgino FL, Cetera C, Laurentiis G. Goserelin versus danazol in the treatment of endometriosis. Clinical and Experimental Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1991;18(2):127‐131. [MDSG # 1775] - PubMed
Kaminski 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kaminski K, Fiegler P, Marr J, Moore C. Treatment of endometriosis with dienogest: preliminary report [Terapia z zastosowaniem dienogestu w leczeniu endometriozy ‐ doniesienie wstepne]. Ginekologia Polska 2001;72(5):299‐304. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Morgante 1999 {published data only}
-
- Morgante G, Ditto A, Marca A, Leo V. Low‐dose danazol after combined surgical and medical therapy reduces the incidence of pelvic pain in women with moderate and severe endometriosis. Human Reproduction 1999;14(9):2371‐74. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 5385] - PubMed
Orwoll 1994 {published data only}
-
- Orwoll ES, Yuspe AA, Buttram VC, Burry KA, Heinrichs WL, Hornstein MD. The effects of nafarelin therapy on hip and spine bone mineral density in endometriosis:a prospective, randomized, double‐blind trial. Fertility & Sterility 1992;58:30. [MDSG # 2692]
-
- Orwoll ES, Yuzpe AA, Burry KA, Heinrich L, Buttram VC, Hornstein MD. Nafarelin therapy in endometriosis: long‐term effects on bone mineral density. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1994;171(5):1221‐25. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 74] - PubMed
Pierce 2000 {published data only}
-
- Pierce SJ, Gazvani MR, Farquharson RG. Long‐term use of gonadotropin‐releasing hormone analogs and hormone replacement therapy in the management of endometriosis: a randomized trial with a 6‐year follow‐up. Fertility and Sterility 2000;74(5):964‐68. - PubMed
Segura 1994 {published data only}
-
- Segura GB, Orozco JATY, Rosales DCO, Origel AV. Mass analysis and bone remodeling in women with pharmacological inhibition of ovarian function. Response to nasal calcitonine. [Analisis de masa y remodelado oseo en mujeres con inhibicion farmacologica de funcion ovarica. Respuesta a calcitonina nasal.]. Ginecologia y obstetricia de Mexico 1994;62:274‐78. - PubMed
Surrey 1995 {published data only}
-
- Surrey E.S, Voigt B, Fournet N, Judd HL. Prolonged gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone agonist treatment of symptomatic endometriosis: the role of cyclic sodium etidronate and low‐dose norethindrone "add‐back" therapy. Fertility and Sterility 1995;63(4):747‐55. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 191] - PubMed
-
- Surrey ES, Fournet N, Voigt B, Judd HL. Effects of sodium etidronate in combination with low‐dose norethidrone in patients administered a long‐acting GnRH agonist: a preliminary report. Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1993;81(4):581‐86. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 546] - PubMed
Surrey 1998 {published data only}
-
- Surrey ES. Add‐back therapy: extending safety and efficacy of GnRH analogues in the gynecologic patient. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 1998;45(suppl 1):31‐4. - PubMed
Tahara 2000 {published data only}
-
- Tahara M, Matsuoka T, Yokoi T, Tasaka K, Kurachi H. Treatment of endometriosis with a decreasing dosage of gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist (nafarelin): a pilot study with low‐dose agonist therapy ("draw‐back" therapy). Fertility and Sterility 2000;73(4):799‐804. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 6023] - PubMed
Taskin 1997 {published data only}
-
- Taskin O, Yalcinoglu AI, Kucuk S, Uryan I, Buhur A, Burak F. Effectiveness of tibolone on hypoestrogenic symptoms incuced by goserelin treatment in patients with endometriosis. Fertility and Sterility 1997;67(1):40‐45. [MDSG # 1707] - PubMed
Uemura 1993 {published data only}
-
- Uemura T, Minaguchi H, Shirasu K, Yosimura Y, Negishi T, Katagiri N, et al. The effect of a sex steroid‐thyroid hormone mixture (metharmon‐F tablets) in preventing climateric symptoms during LH‐RH agonist therapy. Japanese Journal of Fertility and Sterility 1993;38(1):28‐37. [MDSG # 1956]
Uemura 1994 {published data only}
-
- Uemura T, Mohri J, Osada H, Suzuki N, Katagiri N, Minaguchi H. Effect of gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist on the bone mineral density of patients with endometriosis. Fertility & Sterility 1994;62(2):246‐250. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 1316] - PubMed
Ylikorkala 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ylikorkala O, Nilsson G, Hirvonen E, Viinikka L. Evidence of similar increases in bone turnover during nafarelin and danazol use in women with endometriosis. Gynaecological Endocrinology 1990;4(4):251‐260. [MEDLINE: ; MDSG # 1194] - PubMed
Zamberlan 1997 {published data only}
-
- Zamberlan N, Castello R, Gatti D, Rossini M, Braga V, Fracassi E, Adami S. Intermittent etidronate partially prevents bone loss in hirsute hyperandrogenic women treated with GnRH agonist. Osteoporosis International 1997;7(2):133‐37. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Additional references
Audebert 1998
-
- Audebert A, Descampes P, Marret H, et al. Pre or post operative medical treatment with nafarelin in stage III‐IV endometriosis: a French multicentered study. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 1998;79:145‐48. - PubMed
Christiansen 1993
-
- Christiansen C. Prevention and treatment of osteoporosis with hormone replacement therapy. International Journal of Fertility & Menopausal Studies 1993;38(suppl 1):45‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Comite 1989
-
- Comite F, Delman M, Hutchinson‐Williams K, DeCherney AH, Jensen P. Reduced one mass in reproductive‐aged women with endometriosis. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1989;69:837‐42. - PubMed
Cundy 1991
Dodin 1991
-
- Dodin S, Lemay A, Maheux R, Dumont M, Turgot‐Lemay L. Bone mass in endometriosis patients treated with GnRH agonist implant or danazol. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1991;77(3):410‐15. - PubMed
Graves 1925
-
- Graves W P. Relationship of ectopic adenomyomata to ovarian function. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1925;10:665‐70.
Lane 1991
-
- Lane N, Baptista J, Snow‐Harter C. Bone mineral density of the lumbar spine in endometriosis subjects compared to an age‐similar control population. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1991;72(2):510‐14. - PubMed
Nilas 1987
-
- Nilas L, Christiansen C. Bone mass and its relationship to age and the menopause. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1987;65(4):697‐702. - PubMed
Prentice 2003
-
- Prentice A, Deary AJ, Goldbeck‐Wood S, Farquhar C, Smith SK. Gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone analogues for pain associated with endometriosis. The Cochrane Library 2003, Issue 1. - PubMed
Selak 2003
-
- Selak V, Farquhar C, Prentice A, Singla A. Danazol for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis (Cochrane Review). The Cochrane Library 2003, Issue 2. - PubMed
Wahner 1989
-
- Wahner HW. Measurements of bone mass and bone density. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America 1989;18(4):995‐1012. [pub med: 2601246] - PubMed
Wells 2002
-
- Wells G, Tugwell P, Shea B, Guyatt G, Peterson J, Zytaruk N, et al. Meta‐analysis of the efficacy of hormone replacement therapy in treating and preventing osteoporosis in premenopausal women. Endocrine Reviews 2002;23(4):529‐39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

