A role for Arf1 in mitotic Golgi disassembly, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis
- PMID: 14585930
- PMCID: PMC263797
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2234055100
A role for Arf1 in mitotic Golgi disassembly, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis
Abstract
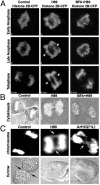
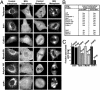
In mitosis, chromosome, cytoskeleton, and organelle dynamics must be coordinated for successful cell division. Here, we present evidence for a role for Arf1, a small GTPase associated with the Golgi apparatus, in the orchestration of mitotic Golgi breakdown, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis. We show that early in mitosis Arf1 becomes inactive and dissociates from Golgi membranes. This is followed by the dispersal of numerous Arf1-dependent peripheral Golgi proteins and subsequent Golgi disassembly. If Arf1 is kept in an active state by treatment with the small molecule H89 or expression of its GTP-locked form, intact Golgi membranes with bound peripheral proteins persist throughout mitosis. These cells enter mitosis but exhibit gross defects in chromosome segregation and cytokinetic furrow ingression. These findings suggest that mitotic Golgi disassembly depends on Arf1 inactivation and is used by the cell to disperse numerous peripheral Golgi proteins for coordinating the behavior of Golgi membranes, chromosomes, and cytoskeleton during mitosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Active ADP-ribosylation factor-1 (ARF1) is required for mitotic Golgi fragmentation.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jul 27;282(30):21829-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611716200. Epub 2007 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17562717 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK phosphorylates GBF1 for mitotic Golgi disassembly.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 15;126(Pt 6):1498-505. doi: 10.1242/jcs.121954. Epub 2013 Feb 15. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23418352
-
Activators and Effectors of the Small G Protein Arf1 in Regulation of Golgi Dynamics During the Cell Division Cycle.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Mar 26;6:29. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00029. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29632863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arf1 GTPase Regulates Golgi-Dependent G2/M Transition and Spindle Organization in Oocyte Meiosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jan;11(4):e2303009. doi: 10.1002/advs.202303009. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38014604 Free PMC article.
-
Building a secretory apparatus: role of ARF1/COPI in Golgi biogenesis and maintenance.Histochem Cell Biol. 1998 May-Jun;109(5-6):449-62. doi: 10.1007/s004180050247. Histochem Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9681627 Review.
Cited by
-
Enterovirus Infection Induces Massive Recruitment of All Isoforms of Small Cellular Arf GTPases to the Replication Organelles.J Virol. 2020 Dec 22;95(2):e01629-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01629-20. Print 2020 Dec 22. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 33087467 Free PMC article.
-
RINT-1 serves as a tumor suppressor and maintains Golgi dynamics and centrosome integrity for cell survival.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jul;27(13):4905-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02396-06. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17470549 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the Rab6A' GTPase in the inactivation of the Mad2-spindle checkpoint.EMBO J. 2006 Jan 25;25(2):278-89. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600929. Epub 2006 Jan 5. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16395330 Free PMC article.
-
Plk1 docking to GRASP65 phosphorylated by Cdk1 suggests a mechanism for Golgi checkpoint signalling.EMBO J. 2005 Feb 23;24(4):753-65. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600569. Epub 2005 Jan 27. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15678101 Free PMC article.
-
Arf1 and ARFGEF2/Sec71 control neuroblast polarity by anchoring nonmuscle myosin II.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Apr 15;122(15):e2419468122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2419468122. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40208939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nasmyth, K., Peters, J. M. & Uhlmann, F. (2000) Science 288, 1379-1384. - PubMed
-
- Warren, G. & Wickner, W. (1996) Cell 84, 395-400. - PubMed
-
- Marsh, B. J. & Howell, K. E. (2002) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 789-795. - PubMed
-
- Shorter, J. & Warren, G. (2002) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 18, 379-420. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson, J. G. & Lippincott-Schwartz, J. (2000) Cell 101, 693-696. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

