EphA3 null mutants do not demonstrate motor axon guidance defects
- PMID: 14585969
- PMCID: PMC262425
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.22.8092-8098.2003
EphA3 null mutants do not demonstrate motor axon guidance defects
Abstract
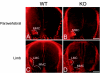
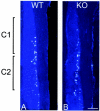
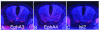
Motor axon projections are topographically ordered. Medial motor column axons project to axial muscles, whereas lateral motor column axons project to limb muscles and, along the rostrocaudal axis of the animal, the more rostral motor neuron pools project to more rostral muscle targets. We have shown that EphA3 is specifically expressed in the developing medial motor column and have postulated that EphA3 might be responsible for directing their axons to axial muscle targets. This hypothesis was supported by our demonstration that EphA3 can direct retinal ganglion cell axon targeting and by studies of ephrin-A5(-/-) mutants that show that EphA receptor signaling controls the topographic innervation of the acromiotrapezius. To test the role of EphA3 in motor axon guidance, we generated an EphA3 null mutant. Retrograde labeling studies in EphA3(-/-) embryos and adults indicate that, contrary to our predictions, EphA3 is not necessary to direct motor axons to axial muscle targets. Our results also demonstrate that ephrin A5's ability to direct topographic innervation of the acromiotrapezius must be mediated through EphA receptors other than, or in addition to, EphA3.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulation of axonal EphA4 forward signaling is involved in the effect of EphA3 on chicken retinal ganglion cell axon growth during retinotectal mapping.Exp Eye Res. 2019 Jan;178:46-60. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Exp Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 30237102
-
High EphA3 expressing ophthalmic trigeminal sensory axons are sensitive to ephrin-A5-Fc: implications for lobe specific axon guidance.Neuroscience. 2005;135(1):97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.05.052. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 16054765
-
Knockdown of ephrin-A5 expression by 40% does not affect motor axon growth or migration into the chick hindlimb.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(12):8362-71. doi: 10.3390/ijms12128362. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22272077 Free PMC article.
-
Crossing the border: molecular control of motor axon exit.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(12):8539-61. doi: 10.3390/ijms12128539. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22272090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterning and axon guidance of cranial motor neurons.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007 Nov;8(11):859-71. doi: 10.1038/nrn2254. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17948031 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Arealization of the Cerebral Cortex.Neuron. 2019 Sep 25;103(6):980-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.07.009. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 31557462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presenilin/γ-secretase-dependent EphA3 processing mediates axon elongation through non-muscle myosin IIA.Elife. 2019 Oct 2;8:e43646. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43646. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31577226 Free PMC article.
-
Polysialylated NCAM and ephrinA/EphA regulate synaptic development of GABAergic interneurons in prefrontal cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2013 Jan;23(1):162-77. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhr392. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Cereb Cortex. 2013. PMID: 22275477 Free PMC article.
-
Segregation of axial motor and sensory pathways via heterotypic trans-axonal signaling.Science. 2008 Apr 11;320(5873):233-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1153758. Science. 2008. PMID: 18403711 Free PMC article.
-
A high-content cellular senescence screen identifies candidate tumor suppressors, including EPHA3.Cell Cycle. 2013 Feb 15;12(4):625-34. doi: 10.4161/cc.23515. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23324396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brambilla, R., and R. Klein. 1995. Telling axons where to grow: a role for eph receptor tyrosine kinases in guidance. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 6:487-495. - PubMed
-
- Brown, A., P. A. Yates, P. Burrola, D. Ortuno, A. Vaidya, T. M. Jessell, S. L. Pfaff, D. D. O'Leary, and G. Lemke. 2000. Topographic mapping from the retina to the midbrain is controlled by relative but not absolute levels of EphA receptor signaling. Cell 102:77-88. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, H., and J. Flanagan. 1994. Identification and cloning of Elf-1, a developmentally expressed ligand for the Mek4 and Sek receptor kinases. Cell 79:157-168. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, H., M. Nakamoto, A. Bergmann, and J. Flanagan. 1995. Complementary gradients in expression and binding of Elf-1 and Mek4 in development of the topographic retinotectal projection map. Cell 82:371-381. - PubMed
-
- Donoghue, M., R. Lewis, J. Merlie, and J. Sanes. 1996. The Eph kinase ligand AL-1 is expressed by rostral muscles and inhibits outgrowth from caudal neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 8:185-198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
