Identification and characterization of a Candida albicans mating pheromone
- PMID: 14585977
- PMCID: PMC262406
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.22.8189-8201.2003
Identification and characterization of a Candida albicans mating pheromone
Abstract
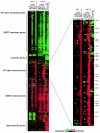
Candida albicans, the most prevalent fungal pathogen of humans, has recently been shown to undergo mating. Here we describe a mating pheromone produced by C. albicans alpha cells and show that the gene which encodes it (MFalpha) is required for alpha cells, but not a cells, to mate. We also identify the receptor for this mating pheromone as the product of the STE2 gene and show that this gene is required for the mating of a cells, but not alpha cells. Cells of the a mating type respond to the alpha mating pheromone by producing long polarized projections, similar to those observed in bona fide mating mixtures of C. albicans a and alpha cells. During this process, transcription of approximately 62 genes is induced. Although some of these genes correspond to those induced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by S. cerevisiae alpha-factor, most are specific to the C. albicans pheromone response. The most surprising class encode cell surface and secreted proteins previously implicated in virulence of C. albicans in a mouse model of disseminated candidiasis. This observation suggests that aspects of cell-cell communication in mating may have been evolutionarily adopted for host-pathogen interactions in C. albicans.
Figures


References
-
- Calderone, R. A., and W. A. Fonzi. 2001. Virulence factors of Candida albicans. Trends Microbiol. 9:327-335. - PubMed
-
- Chang, F., and I. Herskowitz. 1990. Identification of a gene necessary for cell cycle arrest by a negative growth factor of yeast: FAR1 is an inhibitor of a G1 cyclin, CLN2. Cell 63:999-1011. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J., J. Chen, S. Lane, and H. Liu. 2002. A conserved mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is required for mating in Candida albicans. Mol. Microbiol. 46:1335-1344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
