The papillomavirus E8-E2C protein represses DNA replication from extrachromosomal origins
- PMID: 14585992
- PMCID: PMC262328
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.22.8352-8362.2003
The papillomavirus E8-E2C protein represses DNA replication from extrachromosomal origins
Abstract
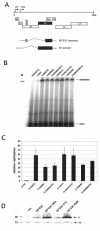
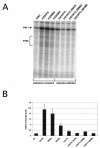
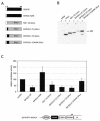
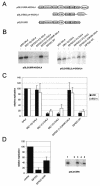
Carcinogenic DNA viruses such as high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV) and Epstein-Barr-Virus (EBV) replicate during persistent infections as low-copy-number plasmids. EBV DNA replication is restricted by host cell replication licensing mechanisms. In contrast, copy number control of HPV genomes is not under cellular control but involves the viral sequence-specific DNA-binding E2 activator and E8-E2C repressor proteins. Analysis of HPV31 mutant genomes revealed that residues outside of the DNA-binding/dimerization domain of E8-E2C limit viral DNA replication, indicating that binding site competition or heterodimerization among E2 and E8-E2C proteins does not contribute to copy number control. Domain swap experiments demonstrated that the amino-terminal 21 amino acids of E8-E2C represent a novel, transferable DNA replication repressor domain, whose activity requires conserved lysine and tryptophan residues. Furthermore, E8-E2C (1-21)-GAL4 fusion proteins inhibited the replication of the plasmid origin of replication of EBV, suggesting that E8-E2C functions as a general replication repressor of extrachromosomal origins. This finding could be important for the development of novel therapies against persistent DNA tumor virus infections.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
