Gamma oscillations induced by kainate receptor activation in the entorhinal cortex in vitro
- PMID: 14586003
- PMCID: PMC6740890
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-30-09761.2003
Gamma oscillations induced by kainate receptor activation in the entorhinal cortex in vitro
Abstract
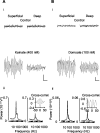
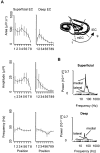
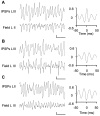
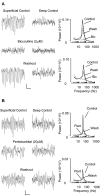
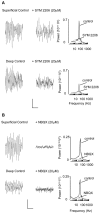
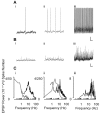
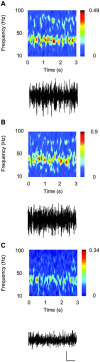
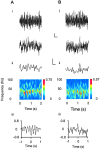
Gamma frequency (30-80 Hz) oscillations are recordable from human and rodent entorhinal cortex. A number of mechanisms used by neuronal networks to generate such oscillations in the hippocampus have been characterized. However, it is as yet unclear as to whether these mechanisms apply to other anatomically disparate brain regions. Here we show that the medial entorhinal cortex (mEC) in isolation in vitro generates gamma frequency oscillations in response to kainate receptor agonists. Oscillations had the same horizontal and laminar spatiotemporal distribution as seen in vivo and in the isolated whole-brain preparation. Oscillations occurred in the absence of input from the hippocampal formation and did not spread to lateral entorhinal regions. Pharmacological similarities existed between oscillations in the hippocampus and mEC in that the latter were also sensitive to GABAA receptor blockade, barbiturates, AMPA receptor blockade, and reduction in gap junctional conductance. Stellate and pyramidal neuron recordings revealed a large GABAergic input consisting of gamma frequency IPSP trains. Fast spiking interneurons in the superficial mEC generated action potentials at gamma frequencies phase locked to the local field. Stellate cells also demonstrated a subthreshold membrane potential oscillation at theta frequencies that was temporally correlated with a theta-frequency modulation in field gamma power. Disruption in this stellate theta frequency oscillation by the hyperpolarisation activated current (Ih) blocker ZD7288 also disrupted theta modulation of field gamma frequency oscillations. We propose that similar cellular and network mechanisms to those seen in the hippocampus generate and modulate persistent gamma oscillations in the entorhinal cortex.
Figures

References
-
- Alonso A, Llinás RR ( 1989) Subthreshold Na +-dependent theta-like rhythmicity in stellate cells of entorhinal cortex layer II. Nature 342: 175–177. - PubMed
-
- Alonso A, Llinás RR ( 1993) Differential electroresponsiveness of stellate and pyramidal-like cells of medial entorhinal cortex layer II. J Neurophysiol 70: 128–143. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Witter MP ( 1989) The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience 31: 571–591. - PubMed
-
- Barth DS, MacDonald KD ( 1996) Thalamic modulation of high-frequency oscillating potentials in auditory cortex. Nature 383: 78–81. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann H, Senitz D ( 2002) Developmental malformations in cerebral structures in “endogenous psychoses.” J Neural Transm 109: 421–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
