E-cadherin controls adherens junctions in the epidermis and the renewal of hair follicles
- PMID: 14592971
- PMCID: PMC275417
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg560
E-cadherin controls adherens junctions in the epidermis and the renewal of hair follicles
Abstract
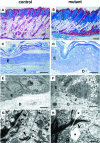
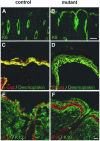
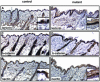
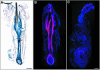
E-cadherin is thought to mediate intercellular adhesion in the mammalian epidermis and in hair follicles as the adhesive component of adherens junctions. We have tested this role of E-cadherin directly by conditional gene ablation in the mouse. We show that postnatal loss of E-cadherin in keratinocytes leads to a loss of adherens junctions and altered epidermal differentiation without accompanying signs of inflammation. Overall tissue integrity and desmosomal structures were maintained, but skin hair follicles were progressively lost. Tumors were not observed and beta-catenin levels were not strongly altered in the mutant skin. We conclude that E-cadherin is required for maintaining the adhesive properties of adherens junctions in keratinocytes and proper skin differentiation. Furthermore, continuous hair follicle cycling is dependent on E-cadherin.
Figures




References
-
- Aberle H., Schwartz,H. and Kemler,R. (1996) Cadherin–catenin complex: protein interactions and their implications for cadherin function. J. Cell. Biochem., 61, 514–523. - PubMed
-
- Boussadia O., Kutsch,S., Hierholzer,A., Delmas,V. and Kemler,R. (2002) E-cadherin is a survival factor for the lactating mouse mammary gland. Mech. Dev., 115, 53–62. - PubMed
-
- Braga V. (2000) Epithelial cell shape: cadherins and small GTPases. Exp. Cell Res., 261, 83–90. - PubMed
-
- Burge S.M. (1992) Hailey–Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br. J. Dermatol., 126, 275–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

