Translocon "pulling" of nascent SecM controls the duration of its translational pause and secretion-responsive secA regulation
- PMID: 14594848
- PMCID: PMC262105
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.22.6719-6722.2003
Translocon "pulling" of nascent SecM controls the duration of its translational pause and secretion-responsive secA regulation
Abstract
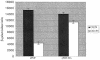
SecA is an ATPase and motor protein that drives protein translocation across the bacterial plasma membrane. In Escherichia coli SecA levels are regulated by the secretion needs of the cell utilizing secM, which encodes a secreted protein. Previous studies demonstrated that this regulation requires a translational pause within secM, whose duration regulates the accessibility of the secA Shine-Dalgarno sequence on secM secA mRNA. Here we provide evidence that translocon "pulling" of nascent SecM is what regulates the duration of the secM translational pause, and thus secA expression levels, thereby providing direct support for this model.
Figures

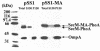
References
-
- Danese, P. N., and T. J. Silhavy. 1998. Targeting and assembly of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Genet. 32:59-94. - PubMed
-
- Davis, N. G., and P. Model. 1985. An artificial anchor domain: hydrophobicity suffices to stop transfer. Cell 41:607-614. - PubMed
-
- Economou, A., and W. Wickner. 1994. SecA promotes preprotein translocation by undergoing ATP-driven cycles of membrane insertion and deinsertion. Cell 78:835-843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

