Mechanism of human dermal fibroblast migration driven by type I collagen and platelet-derived growth factor-BB
- PMID: 14595114
- PMCID: PMC307548
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-05-0352
Mechanism of human dermal fibroblast migration driven by type I collagen and platelet-derived growth factor-BB
Abstract
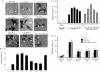
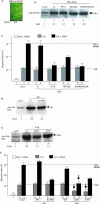
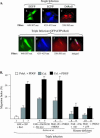
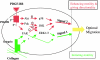
Migration of human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) is critical for skin wound healing. The mechanism remains unclear. We report here that platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) is the major promotility factor in human serum for HDF motility on type I collagen. PDGF-BB recapitulates the full promotility activity of human serum and anti-PDGF neutralizing antibodies completely block it. Although collagen matrix initiates HDF migration without growth factors, PDGF-BB-stimulated migration depends upon attachment of the cells to a collagen matrix. The PDGF-BB's role is to provide directionality and further enhancement for the collagen-initiated HDF motility. To study the collagen and PDGF-BB "dual signaling" in primary HDF, we establish "gene cassettes" plus lentiviral gene delivery approach, in which groups of genes are studied individually or in combination for their roles in HDF migration. Focal adhesion kinase, p21(Rac,CDC42)-activated kinase and Akt are grouped into an upstream kinase gene cassette, and the four major mitogen-activated protein kinases (extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, p38, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5) are grouped into a downstream kinase gene cassette. The experiments demonstrate 1) the genes' individual roles and specificities, 2) their combined effects and sufficiency, and 3) the mechanisms of their intermolecular connections in HDF migration driven by collagen and PDGF-BB.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) regulation of migration and focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation in rabbit aortic vascular smooth muscle cells: roles of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinases.Cardiovasc Res. 1999 Mar;41(3):708-21. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(98)00232-6. Cardiovasc Res. 1999. PMID: 10435043
-
The role of focal adhesion kinase-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt signaling in hepatic stellate cell proliferation and type I collagen expression.J Biol Chem. 2003 Mar 7;278(10):8083-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212927200. Epub 2002 Dec 26. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12502711
-
p38 MAP kinase mediates platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated migration of hepatic myofibroblasts.J Cell Physiol. 2002 Jun;191(3):351-61. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10112. J Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12012331
-
Platelet-derived growth factor. Distinct signal transduction pathways associated with migration versus proliferation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Sep 7;766:416-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb26691.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. PMID: 7486687 Review.
-
Platelet-derived growth factor signaling in mesenchymal cells.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013 Jan 1;18(1):106-19. doi: 10.2741/4090. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013. PMID: 23276912 Review.
Cited by
-
Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) is upregulated by transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and is required for TGF-β-induced hydrogen peroxide production in fibroblasts.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2013 Mar 21;6(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-6-6. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2013. PMID: 23517551 Free PMC article.
-
LRP-1 receptor combines EGFR signalling and eHsp90α autocrine to support constitutive breast cancer cell motility in absence of blood supply.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 14;12(1):12006. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16161-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35835845 Free PMC article.
-
FGF2-induced effects on transcriptome associated with regeneration competence in adult human fibroblasts.BMC Genomics. 2013 Sep 26;14:656. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-656. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24066673 Free PMC article.
-
bFGF and collagen matrix hydrogel attenuates burn wound inflammation through activation of ERK and TRK pathway.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 8;11(1):3357. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82888-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33558597 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Euphrasia officinalis Extract against Ultraviolet B-Induced Photoaging in Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 25;19(11):3327. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113327. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30366440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht-Buehler, G. (1977). The phagokinetic tracks of 3T3 cells. Cell 11, 395-404. - PubMed
-
- Adelmann-Grill, B.C., Wach, F., Cully, Z., Hein, R., and Krieg, T. (1990). Chemotactic migration of normal dermal fibroblasts towards epidermal growth factor and its modulation by platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 51, 322-336. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia, S., Derijard, B., Davis, R.J., and Cerione, R.A. (1995). Cdc42 and PAK-mediated signaling leads to Jun kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 27995-27998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

