Pfeiffer Syndrome type 2--case report
- PMID: 14595512
- PMCID: PMC11108598
- DOI: 10.1590/s1516-31802003000400008
Pfeiffer Syndrome type 2--case report
Abstract
Objective: To report on a case of Pfeiffer Syndrome, with a discussion of the diagnostic characteristics and features of disease types and the differential diagnosis.
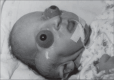
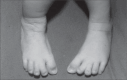
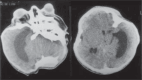
Description: The authors describe a newborn with cloverleaf skull, extreme bilateral exorbitism and choanal atresia, partial syndactyly of the second and third toes and broad medially-deviated big toes. The case reported was Pfeiffer Syndrome type 2, which usually has a poor prognosis.
Comments: Pfeiffer Syndrome is a clinically variable disorder and consists of an autosomal dominantly-inherited osteochondrodysplasia with craniosynostosis. It has been divided into three types. Type 1 is commonly associated with normal intelligence and generally good outcome. Types 2 and 3 generally have severe neurological compromise, poor prognosis, early death and sporadic occurrence. Potential for prolonged useful survival outcome can be achieved in some cases with early aggressive medical and surgical management according to recent literature.
OBJETIVO:: Apresentar relato de um caso de síndrome de Pfeiffer tipo 2, discutindo as características diagnósticas que o diferenciam dos outros tipos e os diagnósticos diferenciais.
DESCRIÇÃO:: Os autores descrevem recém-nascido com crânio em trevo, grave exorbitismo bilateral, atresia de coanas, sindactilia parcial cutânea de segundos e terceiros artelhos, hálux alargados e medialmente desviados, caracterizando o tipo 2 da síndrome de Pfeiffer. Esta síndrome, de manifestação clínica variável, é subdividida classicamente em três tipos distintos. O tipo 2 apresenta pior prognóstico. Chamam atenção para os recentes relatos de literatura, que reportam casos de melhor evolução, quando de abordagem clínica e cirúrgica mais agressiva.
COMENTÁRIOS:: A síndrome de Pfeiffer faz parte das cranioestenoses, constituindo anomalia bastante rara, com herança autossômica dominante. O tipo 1 corresponde à forma menos grave e os tipos 2 e 3 podem ser de ocorrência esporádica e apresentam anomalias muito graves.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Pfeiffer RA. Dominant erbliche akrocephalosyndactylie. Z. Kinderheilk. 1964;90:301–320. - PubMed
-
- Cohen MM. Pfeiffer syndrome update, clinical subtypes, and guidelines for differential diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1993;45(3):300–307. - PubMed
-
- Kroczek RA, Mühlbauer W, Zimmermann I. Cloverleaf skull associated with Pfeiffer syndrome: pathology and management. Eur J Pediatr. 1986;145(5):442–445. - PubMed
-
- Jabs EW. Toward understanding the pathogenesis of craniosynostosis through clinical and molecular correlates. Clin Genet. 1998;53(2):79–86. - PubMed
-
- Rutland P, Pulleyn LJ, Reardon W, et al. Identical mutations in the FGFR2 gene cause both Pfeiffer and Crouzon syndrome phenotypes. Nat Genet. 1995;9(2):173–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

