Lecithin retinol acyltransferase is a founder member of a novel family of enzymes
- PMID: 14596594
- PMCID: PMC5511752
- DOI: 10.1021/bi035370p
Lecithin retinol acyltransferase is a founder member of a novel family of enzymes
Abstract
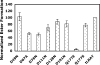
Lecithin retinol acyltransferase (LRAT) catalyzes the reversible esterification of vitamin A using lecithin as the acyl donor. LRAT is the founder member of a new class of enzymes, which include class II tumor suppressors, proteins essential for development, and putative proteases. All of these proteins possess Cys and His residues homologous to C161 and H60 of LRAT. These two residues are shown here to be essential for LRAT activity and are part of a catalytic dyad reminiscent of that found in thiol proteases. However, the local primary sequence contexts of C161 and H60 of LRAT and family are not at all homologous to those found in the approximately 20 thiol protease families. Moreover, LRAT shows pKs of 8.3 and 10.8, compared to approximately 4.0 and 8.5 observed in the thiol proteases. LRAT also contains Gln177 and Asp67 residues, which are largely conserved in the homologues. However, neither of these residues is essential for catalysis. Thiol proteases often contain catalytically essential Asp or Gln residues. It is concluded that LRAT is the founder member of a new class of Cys-His enzymes with diverse functions.
Figures




References
-
- Fulton B, Rando RR. Biochemistry. 1987;26:7938–7945. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald PN, Ong DE. J. Biol. Chem. 1988;263:12478–12482. - PubMed
-
- Saari JC, Bredberg DL. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:8636–8640. - PubMed
-
- Rando RR. Chem. Rev. 2001;101:1881–1896. - PubMed
-
- Zolfaghari R, Ross AC. J. Lipid Res. 2000;41:2024–2034. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

