Critical roles for IFN-beta in lymphoid development, myelopoiesis, and tumor development: links to tumor necrosis factor alpha
- PMID: 14597717
- PMCID: PMC263835
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2230460100
Critical roles for IFN-beta in lymphoid development, myelopoiesis, and tumor development: links to tumor necrosis factor alpha
Abstract
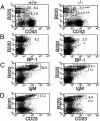
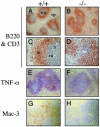
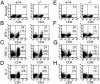
We have generated mice null for IFN-beta and report the diverse consequences of IFN-beta for both the innate and adaptive arms of immunity. Despite no abnormalities in the proportional balance of CD4 and CD8 T cell populations in the peripheral blood, thymus, and spleen of IFN-beta-/- mice, activated lymph node and splenic T lymphocytes exhibit enhanced T cell proliferation and decreased tumor necrosis factor alpha production, relative to IFN-beta+/+ mice. Notably, constitutive and induced expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha is reduced in the spleen and bone marrow (BM) macrophages, respectively, of IFN-beta-/- mice. We also observe an altered splenic architecture in IFN-beta-/- mice and a reduction in resident macrophages. We identify a potential defect in B cell maturation in IFN-beta-/- mice, associated with a decrease in B220+ve/high/CD43-ve BM-derived cells and a reduction in BP-1, IgM, and CD23 expression. Circulating IgM-, Mac-1-, and Gr-1-positive cells are also substantially decreased in IFN-beta-/- mice. The decrease in the numbers of circulating macrophages and granulocytes likely reflects defective maturation of primitive BM hematopoiesis in mice, shown by the reduction of colony-forming units, granulocyte-macrophage. We proceeded to evaluate the in vivo growth of malignant cells in the IFN-beta-/- background and give evidence that Lewis lung carcinoma-specific tumor growth is more aggressive in IFN-beta-/- mice. Taken altogether, our data suggest that, in addition to the direct growth-inhibitory effects on tumor cells, IFN-beta is required during different stages of maturation in the development of the immune system.
Figures
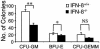
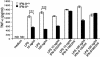
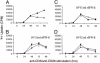

References
-
- Stark, G. R., Kerr, I. M., Williams, B. R. G., Silverman, R. H. & Schreiber, R. D. (1998) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 227-264. - PubMed
-
- Diaz, M. O., Pomykala, H. M., Bohlander, S. K., Maltepe, E., Malik, K., Brownstein, B. & Olopade, O. I. (1994) Genomics 22, 540-552. - PubMed
-
- LaFleur, D. W., Nardelli, B., Tsareva, T., Mather, D., Feng, P., Semenuk, M., Taylor, K., Buergin, M., Chinchilla, D., Roshke, V., et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 39765-39771. - PubMed
-
- Higashi, Y., Sokawa, Y., Watanabe, Y., Kawade, Y., Ohno, S., Takaoka, C. & Taniguchi, T. (1983) J. Biol. Chem. 258, 9522-9529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

