A new Bacteroides conjugative transposon that carries an ermB gene
- PMID: 14602600
- PMCID: PMC262298
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.11.6455-6463.2003
A new Bacteroides conjugative transposon that carries an ermB gene
Abstract
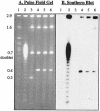
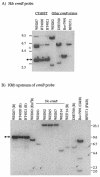
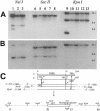
The erythromycin resistance gene ermB has been found in a variety of gram-positive bacteria. This gene has also been found in Bacteroides species but only in six recently isolated strains; thus, the gene seems to have entered this genus only recently. One of the six Bacteroides ermB-containing isolates, WH207, could transfer ermB to Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain BT4001 by conjugation. WH207 was identified as a Bacteroides uniformis strain based on the sequence of its 16S rRNA gene. Results of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis experiments demonstrated that the transferring element was normally integrated into the Bacteroides chromosome. The element was estimated from pulsed-field gel data to be about 100 kb in size. Since the element appeared to be a conjugative transposon (CTn), it was designated CTnBST. CTnBST was able to mobilize coresident plasmids and the circular form of the mobilizable transposon NBU1 to Bacteroides and Escherichia coli recipients. A 13-kb segment that contained ermB was cloned and sequenced. Most of the open reading frames in this region had little similarity at the amino acid sequence level to any proteins in the sequence databases, but a 1,723-bp DNA segment that included a 950-bp segment downstream of ermB had a DNA sequence that was virtually identical to that of a segment of DNA found previously in a Clostridium perfringens strain. This finding, together with the finding that ermB is located on a CTn, supports the hypothesis that CTnBST could have entered Bacteroides from some other genus, possibly from gram-positive bacteria. Moreover, this finding supports the hypothesis that many transmissible antibiotic resistance genes in Bacteroides are carried on CTns.
Figures

References
-
- Birren, B. W., and E. H. C. Lai. 1993. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis: a practical guide. Academic Press, San Diego, Calif.
-
- Boerlin, P., A. P. Burnens, J. Frey, P. Kuhnert, and J. Nicolet. 2001. Molecular epidemiology and genetic linkage of macrolide and aminoglycoside resistance in Staphylococcus intermedius of canine origin. Vet. Microbiol. 79:155-169. - PubMed
-
- Ceglowski, P., and J. C. Alonso. 1994. Gene organization of the Streptococcus pyogenes plasmid pDB101: sequence analysis of the orf eta-copS region. Gene 145:33-39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

