Mycobacterium xenopi and drinking water biofilms
- PMID: 14602661
- PMCID: PMC262275
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.11.6946-6948.2003
Mycobacterium xenopi and drinking water biofilms
Abstract
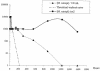
The ability of Mycobacterium xenopi to colonize an experimental drinking water distribution system (a Propella reactor) was investigated. M. xenopi was present in the biofilm within an hour following its introduction. After 9 weeks, it was always present in the outlet water (1 to 10 CFU 100 ml(-1)) and inside the biofilm (10(2) to 10(3) CFU cm(-2)). Biofilms may be considered reservoirs for the survival of M. xenopi.
Figures
References
-
- Appenzeller, B. M., M. Batté, L. Mathieu, J. C. Block, V. Lahoussine, J. Cavard, and D. Gatel. 2001. Effect of adding phosphate to drinking water on bacterial growth in slightly and highly corroded pipes. Water Res. 35:1100-1105. - PubMed
-
- Astagneau, P., N. Desplaces, V. Vincent, V. Chicheportiche, H. Bortherel, S. Maugat, K. Lebascle, P. Leonard, J. C. Desenclos, J. Grosset, J. M. Ziza, and G. Brücker. 2001. Mycobacterium xenopi spinal infections after discovertebral surgery: investigation and screening of a large outbreak. Lancet 358:747-751. - PubMed
-
- Bardouniotis, E., H. Ceri, and M. E. Olson. 2003. Biofilm formation and biocide susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium fortuitum and Mycobacterium marinum. Curr. Microbiol. 46:28-32. - PubMed
-
- Hall-Stoodley, L., and H. M. Lappin-Scott. 1998. Biofilm formation by the rapidly growing mycobacterial species Mycobacterium fortuitum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 168:77-84. - PubMed
-
- Jiva, T. M., H. M. Jacoby, L. A. Weymouth, D. A. Kaminski, and A. C. Portmore. 1997. Mycobacterium xenopi: innocent bystander or emerging pathogen? Clin. Infect. Dis. 24:226-232. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases