Lmx1b, Pet-1, and Nkx2.2 coordinately specify serotonergic neurotransmitter phenotype
- PMID: 14602809
- PMCID: PMC6740868
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-31-09961.2003
Lmx1b, Pet-1, and Nkx2.2 coordinately specify serotonergic neurotransmitter phenotype
Abstract
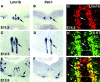
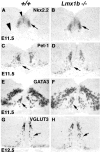
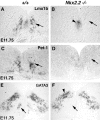
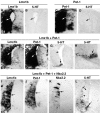
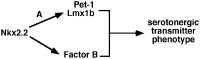
Serotonergic (5-HT) neurons in the brainstem modulate a wide range of physiological processes and behaviors. Two transcription factor genes, Pet-1 and Nkx2.2, are necessary but not sufficient to specify the 5-HT transmitter phenotype. Here we show that the Lim class homeobox gene Lmx1b is required for proper formation of the entire 5-HT system in the hindbrain, as indicated by the loss of expression of genes necessary for serotonin synthesis and transport in Lmx1b null mice. Lmx1b and Pet1 act downstream of Nkx2.2, and their expression is independently regulated at the time when 5-HT transmitter phenotype is specified. Ectopic expression of Lmx1b plus Pet-1 is able to induce formation of 5-HT cells in the most ventral spinal cord, where Nkx2.2 is normally expressed. Combined expression of all three genes, Lmx1b, Pet-1, and Nkx2.2, drives 5-HT differentiation in the dorsal spinal cord. Our studies therefore define a molecular pathway necessary and sufficient to specify the serotonergic neurotransmitter phenotype.
Figures

References
-
- Adams KA, Maida JM, Golden JA, Riddle RD ( 2000) The transcription factor Lmx1b maintains Wnt1 expression within the isthmic organizer. Development 127: 1857-1867. - PubMed
-
- Asbreuk CH, Vogelaar CF, Hellemons A, Smidt MP, Burbach JP ( 2002) CNS expression pattern of Lmx1b and coexpression with ptx genes suggest functional cooperativity in the development of forebrain motor control systems. Mol Cell Neurosci 21: 410-420. - PubMed
-
- Blakely RD, Berson HE, Fremeau RTJ, Caron MG, Peek MM, Prince HK, Bradley CC ( 1991) Cloning and expression of a functional serotonin transporter from rat brain. Nature 354: 66-70. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Sussel L, Serup P, Hartigan-O'Connor D, Jessell TM, Rubenstein J, Ericson J ( 1999) Homeobox gene Nkx2.2 and specification of neuronal identity by graded Sonic hedgehog signalling. Nature 398: 622-627. - PubMed
-
- Chang AS, Chang SM, Starnes DM, Schroeter S, Bauman AL, Blakely RD ( 1996) Cloning and expression of the mouse serotonin transporter. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 43: 185-192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
