EARLY FLOWERING 4 functions in phytochrome B-regulated seedling de-etiolation
- PMID: 14605220
- PMCID: PMC300710
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.030007
EARLY FLOWERING 4 functions in phytochrome B-regulated seedling de-etiolation
Abstract
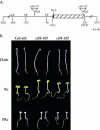
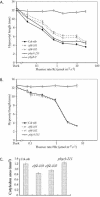
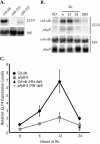
To define the functions of genes previously identified by expression profiling as being rapidly light induced under phytochrome (phy) control, we are investigating the seedling de-etiolation phenotypes of mutants carrying T-DNA insertional disruptions at these loci. Mutants at one such locus displayed reduced responsiveness to continuous red, but not continuous far-red light, suggesting a role in phyB signaling but not phyA signaling. Consistent with such a role, expression of this gene is induced by continuous red light in wild-type seedlings, but the level of induction is strongly reduced in phyB-null mutants. The locus encodes a novel protein that we show localizes to the nucleus, thus suggesting a function in light-regulated gene expression. Recently, this locus was identified as EARLY FLOWERING 4, a gene implicated in floral induction and regulating the expression of the gene CIRCADIAN CLOCK-ASSOCIATED 1. Together with these previous data, our findings suggest that EARLY FLOWERING 4 functions as a signaling intermediate in phy-regulated gene expression involved in promotion of seedling de-etiolation, circadian clock function, and photoperiod perception.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression profiling of phyB mutant demonstrates substantial contribution of other phytochromes to red-light-regulated gene expression during seedling de-etiolation.Plant J. 2004 Jun;38(5):725-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02084.x. Plant J. 2004. PMID: 15144375
-
Arabidopsis PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR7 is a signaling intermediate in phytochrome-regulated seedling deetiolation and phasing of the circadian clock.Plant Cell. 2003 Nov;15(11):2654-65. doi: 10.1105/tpc.015065. Epub 2003 Oct 16. Plant Cell. 2003. PMID: 14563930 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of phyC mutants in Arabidopsis reveals complex crosstalk between phytochrome signaling pathways.Plant Cell. 2003 Sep;15(9):1962-80. doi: 10.1105/tpc.012971. Plant Cell. 2003. PMID: 12953104 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling networks in the plant circadian system.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2001 Oct;4(5):429-35. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(00)00196-5. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2001. PMID: 11597501 Review.
-
Dancing in the dark: darkness as a signal in plants.Plant Cell Environ. 2017 Nov;40(11):2487-2501. doi: 10.1111/pce.12900. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Plant Cell Environ. 2017. PMID: 28044340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A constitutive shade-avoidance mutant implicates TIR-NBS-LRR proteins in Arabidopsis photomorphogenic development.Plant Cell. 2006 Nov;18(11):2919-28. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.038810. Epub 2006 Nov 17. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 17114357 Free PMC article.
-
The Evening Complex and the Chromatin-Remodeling Factor PICKLE Coordinately Control Seed Dormancy by Directly Repressing DOG1 in Arabidopsis.Plant Commun. 2019 Dec 3;1(2):100011. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2019.100011. eCollection 2020 Mar 9. Plant Commun. 2019. PMID: 33404551 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Translational Mechanisms of Plant Circadian Regulation.Genes (Basel). 2021 Feb 24;12(3):325. doi: 10.3390/genes12030325. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DIE NEUTRALIS and LATE BLOOMER 1 contribute to regulation of the pea circadian clock.Plant Cell. 2009 Oct;21(10):3198-211. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.067223. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Plant Cell. 2009. PMID: 19843842 Free PMC article.
-
A novel molecular recognition motif necessary for targeting photoactivated phytochrome signaling to specific basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors.Plant Cell. 2004 Nov;16(11):3033-44. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.025643. Epub 2004 Oct 14. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15486100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alabadi D, Oyama T, Yanovski MJ, Harmon FG, Mas P, Kay SA (2001) Reciprocal regulation between TOC1 and LHY/CCA1. Science 293: 880-883 - PubMed
-
- Devlin PF (2002) Signs of the time: environmental input to the circadian clock. J Exp Biol 53: 1535-1550 - PubMed
-
- Doyle MR, Davis SJ, Bastow RM, McWatters HG, Kozma-Bognár L, Nagy F, Miller AJ, Amasino RM (2002) The ELF4 gene controls circadian rhythms and flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 419: 74-77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

