Feasibility of 186Re-radioimmunotherapy for treatment in an adjuvant setting of colon cancer
- PMID: 14605881
- PMCID: PMC12161974
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-003-0453-7
Feasibility of 186Re-radioimmunotherapy for treatment in an adjuvant setting of colon cancer
Abstract
Purpose: (186)Re displays abundant intermediate energy beta emission, and possesses an appropriate physical half-life of 3.7 days. We compared the efficacy of radioimmunotherapy (RIT) with an anti-colorectal cancer monoclonal IgG1, (186)Re-A7, with that of RIT employing (131)I in a mouse liver metastasis model.
Methods: Liver metastases were established by intrasplenic injection of LS180 human colon cancer cells. Based on the results of toxicity assessment with escalated administration doses, 21 MBq (186)Re-A7 and 7 MBq (131)I-A7 were chosen as maximum tolerated doses. In the first experiment, mice underwent RIT at 2 weeks when metastases attain a diameter of several millimeters, and were killed 2 weeks later to assess metastatic burden in the liver. In the second experiment, RIT was conducted at 1 week when metastases of several hundred micrometers in diameter were observed, and survival of mice was examined.
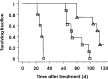
Results: (186)Re-A7 RIT inhibited the growth of liver metastases better than (131)I-A7 RIT ( P<0.02). Furthermore, (186)Re-A7 RIT induced better improvement in survival of mice than (131)I-A7 RIT ( P<0.002). (186)Re-A7 RIT caused slightly more severe myelotoxicity in mice, but they eventually recovered. Radiation dose estimation demonstrated a significant advantage of (186)Re-A7 RIT over (131)I-A7 RIT.
Conclusion: These results support the use of RIT with (186)Re-MAb in an adjuvant setting in cases involving minimal disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Radioimmunotherapy with 186Re-labeled monoclonal antibody to treat liver metastases of colon cancer cells in nude mice.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2002 Dec;17(6):681-7. doi: 10.1089/108497802320970299. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2002. PMID: 12537672
-
Benefits of combined radioimmunotherapy and anti-angiogenic therapy in a liver metastasis model of human colon cancer cells.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002 Dec;29(12):1669-74. doi: 10.1007/s00259-002-0997-9. Epub 2002 Oct 2. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002. PMID: 12458402
-
Efficacy, toxicity and mode of interaction of combination radioimmunotherapy with 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer xenografts.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1999 Nov;125(11):630-6. doi: 10.1007/s004320050326. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1999. PMID: 10541970 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Pre-operative endometrial thinning agents before endometrial destruction for heavy menstrual bleeding.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Nov 15;2013(11):CD010241. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010241.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24234875 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Radiotherapy and wound healing.Int Wound J. 2005 Jun;2(2):112-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4801.2005.00079.x. Int Wound J. 2005. PMID: 16722862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regional radiochemotherapy using in situ hydrogel.Pharm Res. 2005 May;22(5):776-83. doi: 10.1007/s11095-005-2594-7. Epub 2005 May 17. Pharm Res. 2005. PMID: 15906173
-
Intraperitoneal radioimmunotherapy in treating peritoneal carcinomatosis of colon cancer in mice compared with systemic radioimmunotherapy.Cancer Sci. 2003 Jul;94(7):650-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01498.x. Cancer Sci. 2003. PMID: 12841877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beaumier PL, Venkatensan P, Vanderheyden JL, Burgua WD, Kunz LL, Fritzberg AR, Abrams PG, Morgan AC Jr (1991) 186Re radioimmunotherapy of small cell lung carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Res 81:676–681 - PubMed
-
- Behr TM, Sharkey RM, Juweid M, Dunn RM, Ying Z, Zhang CH, Siegel JA, Goldenberg DM (1997) Variables influencing tumor dosimetry in radioimmunotherapy of CEA-expressing cancers with anti-CEA and anti-mucin monoclonal antibodies. J Nucl Med 38:409–417 - PubMed
-
- Behr TM, Blumenthal RD, Memtsoudis S, Sharkey RM, Gratz S, Becker W, Goldenberg DM (2000) Cure of metastatic human colonic cancer in mice with radiolabeled monoclonal antibody fragments. Clin Cancer Res 6:4900–4907 - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal RD, Sharkey RM, Haywood L, Natale AM, Wong GY, Siegel JA, Kennel SJ, Goldenberg DM (1992) Targeted therapy of athymic mice bearing GW-39 human colonic cancer micrometastases with 131I-labeled monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res 52:6036–6044 - PubMed
-
- Dunn RM, Juweid M, Sharkey RM, Behr TM, Goldenberg DM (1997) Can occult metastases be treated by radioimmunotherapy? Cancer [Suppl] 80:2656–2659 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

