Study on hepatocellular carcinoma-associated hepatic arteriovenous shunt using multidetector CT
- PMID: 14606075
- PMCID: PMC4656520
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2455
Study on hepatocellular carcinoma-associated hepatic arteriovenous shunt using multidetector CT
Abstract
Aim: To investigate multidetector CT (MDCT) findings of hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC)- associated hepatic arteriovenous shunt (HAVS) and to evaluate their clinical significance.
Methods: Thin-slice and dynamic enhancement MDCT of HAVS was performed on 56 patients with HCC. MDCT findings, including those of portal veins, hepatic veins, superior mesenteric veins, splenic veins, HCC foci, liver parenchyma without HCC foci, spleens, and thromboses in portal veins and hepatic veins, were all confirmed by digital subtract angiography and analyzed.
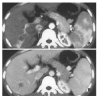
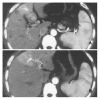
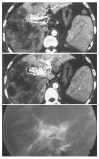
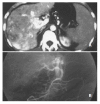
Results: MDCT demonstrated earlier enhancement of main portal trunks and/or the first order branches than that of superior mesenteric veins or splenic veins (n=31). One patient had strong early enhancement of left hepatic vein with thromboses in left hepatic vein and upper part of inferior vena cava and 1 patient had transient patchy enhancement peripheral to HCC foci in late hepatic arterial phase among them. It demonstrated stronger opacification of main portal trunks and/or the first order branches than that of superior mesenteric veins or splenic veins (n=18), and earlier enhancement of the second order and smaller branches of portal veins than that of main portal trunks (n=4), stronger opacification of the second order and smaller branches of portal veins than that of main portal trunks (n=3), with transient patchy enhancement (n=3) or wedge-shaped enhancement (n=4) peripheral to HCC foci in late hepatic arterial phase. Enhancement degree of HCC foci was all decreased. As for 49 patients with severe or moderate shunts, enhancement degree of liver parenchyma without HCC foci was increased with heterogeneous density, but enhancement degree of spleens was decreased. There were thromboses in main portal trunks and/or the first order branches in 32 patients.
Conclusion: The main MDCT findings of HCC-associated HAVS are earlier enhancement and stronger opacification of portal veins and/or hepatic veins. Understanding of these findings will contribute to the diagnosis and prognosis of the disease and improve therapy for the patients.
Figures
References
-
- Mortele KJ, McTavish J, Ros PR. Current techniques of computed tomography. Helical CT, multidetector CT, and 3D reconstruction. Clin Liver Dis. 2002;6:29–52. - PubMed
-
- Chen JH, Chai JW, Huang CL, Hung HC, Shen WC, Lee SK. Proximal arterioportal shunting associated with hepatocellular carcinoma: features revealed by dynamic helical CT. AJR. Am J Roentgenol. 1999;172:403–407. - PubMed
-
- Kim TK, Choi BI, Han JK, Chung JW, Park JH, Han MC. Nontumorous arterioportal shunt mimicking hypervascular tumor in cirrhotic liver: two-phase spiral CT findings. Radiology. 1998;208:597–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

