Novel form of adaptation in mouse retinal rods speeds recovery of phototransduction
- PMID: 14610022
- PMCID: PMC2229593
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200308938
Novel form of adaptation in mouse retinal rods speeds recovery of phototransduction
Abstract
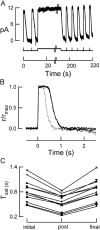
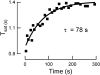
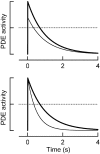
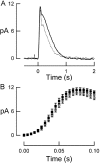
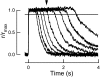
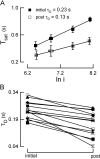
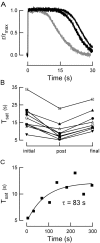
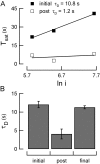
Photoreceptors of the retina adapt to ambient light in a manner that allows them to detect changes in illumination over an enormous range of intensities. We have discovered a novel form of adaptation in mouse rods that persists long after the light has been extinguished and the rod's circulating dark current has returned. Electrophysiological recordings from individual rods showed that the time that a bright flash response remained in saturation was significantly shorter if the rod had been previously exposed to bright light. This persistent adaptation did not decrease the rate of rise of the response and therefore cannot be attributed to a decrease in the gain of transduction. Instead, this adaptation was accompanied by a marked speeding of the recovery of the response, suggesting that the step that rate-limits recovery had been accelerated. Experiments on knockout rods in which the identity of the rate-limiting step is known suggest that this adaptive acceleration results from a speeding of G protein/effector deactivation.
Figures
References
-
- Burns, M.E., A. Mendez, J. Chen, and D.A. Baylor. 2002. Dynamics of cyclic GMP synthesis in retinal rods. Neuron. 36:81–91. - PubMed
-
- Calvert, P.D., V.I. Govardovskii, N. Krasnoperova, R.E. Anderson, J. Lem, and C.L. Makino. 2001. Membrane protein diffusion sets the speed of rod phototransduction. Nature. 411:90–94. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C.K., M.E. Burns, W. He, T.G. Wensel, D.A. Baylor, and M.I. Simon. 2000. Slowed recovery of rod photoresponse in mice lacking the GTPase accelerating protein RGS9-1. Nature. 403:557–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

