Usefulness of monitoring lung function in asthma
- PMID: 14612375
- PMCID: PMC1719360
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.88.11.1021
Usefulness of monitoring lung function in asthma
Abstract
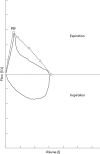
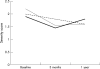
There is no firm evidence from randomised controlled trials that routine monitoring of lung function improves asthma control in children. Guidelines for management of asthma consistently recommend routine home monitoring of peak expiratory flow (PEF) in each patient. However, changes in PEF poorly reflect changes in asthma activity, PEF diaries are kept very unreliably, and self management programmes including PEF monitoring are no more effective than programmes solely based on education and symptom monitoring. PEF diaries may still be useful in isolated cases of diagnostic uncertainty, in the identification of exacerbating factors, and in the rare case of children perceiving airways obstruction poorly and exacerbating frequently and severely. If a reliable assessment of airways obstruction in asthma is needed, forced expiratory flow-volume curves are the preferred method. Monitoring of hyperresponsiveness and nitric oxide cannot be recommended for routine use at present. Clinical judgement and expiratory flow-volume loops remain the cornerstone of monitoring asthma in secondary care.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Monitoring asthma in childhood: lung function, bronchial responsiveness and inflammation.Eur Respir Rev. 2015 Jun;24(136):204-15. doi: 10.1183/16000617.00003914. Eur Respir Rev. 2015. PMID: 26028633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in peak expiratory flow indices as a proxy for changes in bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Dutch Chronic Non-Specific Lung Disease study group.Eur Respir J. 2000 Aug;16(2):220-5. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.16b07.x. Eur Respir J. 2000. PMID: 10968495 Clinical Trial.
-
Peak flow variation in childhood asthma: relationship to symptoms, atopy, airways obstruction and hyperresponsiveness. Dutch CNSLD Study Group.Eur Respir J. 1997 Jun;10(6):1242-7. doi: 10.1183/09031936.97.10061242. Eur Respir J. 1997. PMID: 9192923
-
Testing bronchial hyper-responsiveness: provocation or peak expiratory flow variability?Br J Gen Pract. 1997 Aug;47(421):487-92. Br J Gen Pract. 1997. PMID: 9302787 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Role of peak expiratory flow in the assessment and management of asthma in children].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Jun;23(6):645-649. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2101134. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34130789 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Monitoring asthma in childhood: lung function, bronchial responsiveness and inflammation.Eur Respir Rev. 2015 Jun;24(136):204-15. doi: 10.1183/16000617.00003914. Eur Respir Rev. 2015. PMID: 26028633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Will symptom-based therapy be effective for treating asthma in children?Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013 Oct;13(5):421-6. doi: 10.1007/s11882-013-0364-x. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013. PMID: 23775350 Review.
-
Reliability and validity of childhood asthma control test in a population of Chinese asthmatic children.Qual Life Res. 2008 May;17(4):585-93. doi: 10.1007/s11136-008-9335-4. Qual Life Res. 2008. PMID: 18389383
-
Is spirometry essential in diagnosing asthma? Yes.Br J Gen Pract. 2016 Sep;66(650):484. doi: 10.3399/bjgp16X686953. Br J Gen Pract. 2016. PMID: 27563136 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The need for standardisation of peak flow charts.Thorax. 2005 Feb;60(2):164-7. doi: 10.1136/thx.2004.030437. Thorax. 2005. PMID: 15681507 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
