Acetylation of androgen receptor enhances coactivator binding and promotes prostate cancer cell growth
- PMID: 14612401
- PMCID: PMC262657
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.23.8563-8575.2003
Acetylation of androgen receptor enhances coactivator binding and promotes prostate cancer cell growth
Abstract
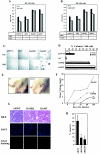
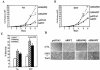
Modification by acetylation occurs at epsilon-amino lysine residues of histones and transcription factors. Unlike phosphorylation, a direct link between transcription factor acetylation and cellular growth or apoptosis has not been established. We show that the nuclear androgen receptor (AR), a DNA-binding transcriptional regulator, is acetylated in vivo. The acetylation of the AR is induced by ligand dihydrotestosterone and by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors in living cells. Direct AR acetylation augmented p300 binding in vitro. Constructs mimicking neutral polar substitution acetylation (AR(K630Q), AR(K630T)) enhanced p300 binding and reduced N-CoR/HDAC/Smad3 corepressor binding, whereas charged residue substitution (AR(K630R)) reduced p300 binding and enhanced corepressor binding. The AR acetylation mimics promoted cell survival and growth of prostate cancer cells in soft agar and in nude mice and augmented transcription of a subset of growth control target gene promoters. Thus, transcription factor acetylation regulates coactivator/corepressor complex binding, altering expression of specific growth control genes to promote aberrant cellular growth in vivo.
Figures
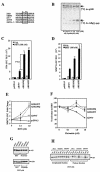
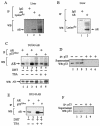
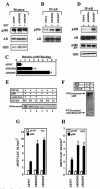
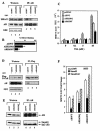

References
-
- Abate-Shen, C., and M. M. Shen. 2000. Molecular genetics of prostate cancer. Genes Dev. 14:2410-2434. - PubMed
-
- Alland, L., R. Muhle, H. J. Hou, J. Potes, L. Chin, N. Schreiber-Agus, and R. A. DePinho. 1997. Role for N-CoR and histone deacetylase in Sin3-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature 387:49-55. - PubMed
-
- Chen, D., H. Ma, H. Hong, S. S. Koh, S. M. Huang, B. T. Schurter, D. W. Aswad, and M. R. Stallcup. 1999. Regulation of transcription by a protein methyltransferase. Science 284:2174-2177. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J. D., and R. M. Evans. 1995. A transcriptional co-repressor that interacts with nuclear hormone receptors. Nature 377:454-457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA075503/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA75503/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA65647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK065220/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG2033/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA051008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA070896/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA51008-13/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R21DK065220-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA83979/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA70896/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA86072/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA086072/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA083979/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
