Retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion to PML affects its transcriptional and chromatin-remodeling properties
- PMID: 14612419
- PMCID: PMC262687
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.23.8795-8808.2003
Retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion to PML affects its transcriptional and chromatin-remodeling properties
Abstract
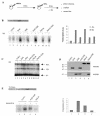
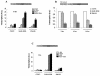
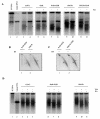
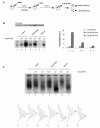
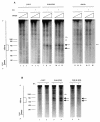
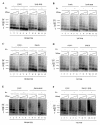
PML-RAR is an oncogenic transcription factor forming in acute promyelocytic leukemias (APL) because of a chromosomal translocation. Without its ligand, retinoic acid (RA), PML-RAR functions as a constitutive transcriptional repressor, abnormally associating with the corepressor-histone deacetylase complex and blocking hematopoietic differentiation. In the presence of pharmacological concentrations of RA, PML-RAR activates transcription and stimulates differentiation. Even though it has been suggested that chromatin alteration is important for APL onset, the PML-RAR effect on chromatin of target promoters has not been investigated. Taking advantage of the Xenopus oocyte system, we compared the wild-type transcription factor RARalpha with PML-RAR as both transcriptional regulators and chromatin structure modifiers. Without RA, we found that PML-RAR is a more potent transcriptional repressor that does not require the cofactor RXR and produces a closed chromatin configuration. Surprisingly, repression by PML-RAR occurs through a further pathway that is independent of nucleosome deposition and histone deacetylation. In the presence of RA, PML-RAR is a less efficient transcriptional activator that is unable to modify the DNA nucleoprotein structure. We propose that PML-RAR, aside from its ability to recruit aberrant quantities of histone deacetylase complexes, has acquired additional repressive mechanisms and lost important activating functions; the comprehension of these mechanisms might reveal novel targets for antileukemic intervention.
Figures

References
-
- Benedetti, L., A. A. Levin, B. M. Scicchitano, F. Grignani, G. Allanby, D. Diverio, F. Lo Coco, G. Avvisati, M. Ruthardt, S. Adamo, P. G. Pelicci, and C. Nervi. 1997. Characterization of the retinoid binding properties of the major fusion products present in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Blood 90:1175-1185. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H., R. J. Lin, W. Xie, D. Wilpitz, and R. M. Evans. 1999. Regulation of hormone-induced histone hyperacetylation and gene activation via acetylation of an acetylase. Cell 98:675-686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
