Recruitment of SWI/SNF by Gcn4p does not require Snf2p or Gcn5p but depends strongly on SWI/SNF integrity, SRB mediator, and SAGA
- PMID: 14612422
- PMCID: PMC262668
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.23.8829-9945.2003
Recruitment of SWI/SNF by Gcn4p does not require Snf2p or Gcn5p but depends strongly on SWI/SNF integrity, SRB mediator, and SAGA
Abstract
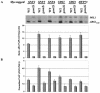
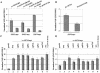
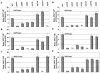
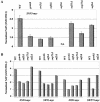
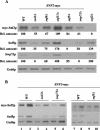
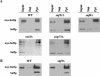
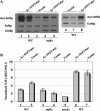
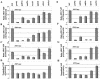
The nucleosome remodeling complex SWI/SNF is a coactivator for yeast transcriptional activator Gcn4p. We provide strong evidence that Gcn4p recruits the entire SWI/SNF complex to its target genes ARG1 and SNZ1 but that SWI/SNF is dispensable for Gcn4p binding to these promoters. It was shown previously that Snf2p/Swi2p, Snf5p, and Swi1p interact directly with Gcn4p in vitro. However, we found that Snf2p is not required for recruitment of SWI/SNF by Gcn4p nor can Snf2p be recruited independently of other SWI/SNF subunits in vivo. Snf5p was not recruited as an isolated subunit but was required with Snf6p and Swi3p for optimal recruitment of other SWI/SNF subunits. The results suggest that Snf2p, Snf5p, and Swi1p are recruited only as subunits of intact SWI/SNF, a model consistent with the idea that Gcn4p makes multiple contacts with SWI/SNF in vivo. Interestingly, Swp73p is necessary for efficient SWI/SNF recruitment at SNZ1 but not at ARG1, indicating distinct subunit requirements for SWI/SNF recruitment at different genes. Optimal recruitment of SWI/SNF by Gcn4p also requires specific subunits of SRB mediator (Gal11p, Med2p, and Rox3p) and SAGA (Ada1p and Ada5p) but is independent of the histone acetyltransferase in SAGA, Gcn5p. We suggest that SWI/SNF recruitment is enhanced by cooperative interactions with subunits of SRB mediator and SAGA recruited by Gcn4p to the same promoter but is insensitive to histone H3 acetylation by Gcn5p.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
