A phase II trial of capecitabine (Xeloda) in recurrent ovarian cancer
- PMID: 14612890
- PMCID: PMC2394434
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601381
A phase II trial of capecitabine (Xeloda) in recurrent ovarian cancer
Abstract
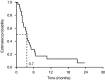
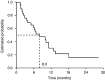
Oral capecitabine is a highly active, well-tolerated and convenient treatment for breast and colorectal cancer. This trial assessed the efficacy and safety of single-agent capecitabine in patients with previously treated ovarian cancer. A total of 29 patients with platinum-pretreated relapsed ovarian cancer were enrolled in this prospective, open-label, single-centre, phase II study. Patients received oral capecitabine 1250 mg m(-2) twice daily on days 1-14 of a 21-day cycle. Tumour response was evaluated using serum CA125. Out of 29 enrolled patients, 28 were evaluable, and a response was observed in eight patients (29%, 95% confidence interval (CI), 13-49%). Median progression-free and overall survivals were 3.7 (95% CI, 2.8-4.6) and 8.0 (95% CI, 4.1-11.8) months, respectively. After 6 months of treatment, 28% (95% CI, 13-48%) of patients remained progression-free and 62% (95% CI, 42-79%) were still alive. The most common clinical adverse events were hand-foot syndrome (HFS), nausea and diarrhoea. Grade 3 HFS occurred in 14% of patients, grade 3 vomiting in 10%. Efficacy and safety of capecitabine compare favourably with other monotherapies in platinum-refractory epithelial ovarian cancer. The convenience and improved safety profile of capecitabine compared with intravenous. regimens make it an ideal agent for administration in the outpatient setting.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A phase II study of capecitabine in the treatment of ovarian cancer resistant or refractory to platinum therapy: a multicentre Italian trial in ovarian cancer (MITO-6) trial.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;64(5):1021-7. doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-0958-0. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19266200 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase II trial of oral capecitabine in patients with platinum--and taxane--refractory ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer.Gynecol Oncol. 2006 Sep;102(3):468-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.12.040. Epub 2006 Mar 3. Gynecol Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16516276 Clinical Trial.
-
[Experience with xeloda (capecitabine) as a component of chemotherapy for relapsing cisplatin-resistant ovarian tumors].Vopr Onkol. 2003;49(2):193-7. Vopr Onkol. 2003. PMID: 12785204 Russian.
-
Capecitabine: a review.Clin Ther. 2005 Jan;27(1):23-44. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.01.005. Clin Ther. 2005. PMID: 15763604 Review.
-
Capecitabine: a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the management of advanced breast cancer.Drugs. 2003;63(2):217-36. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363020-00009. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12515569 Review.
Cited by
-
The anti-aging factor α-klotho during human pregnancy and its expression in pregnancies complicated by small-for-gestational-age neonates and/or preeclampsia.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014 Mar;27(5):449-57. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2013.818652. Epub 2013 Aug 19. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014. PMID: 23808483 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of the oral fluorouracil pro-drug capecitabine in cancer treatment: a review.Molecules. 2008 Aug 27;13(8):1897-922. doi: 10.3390/molecules13081897. Molecules. 2008. PMID: 18794792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Oral Metronomic Chemotherapy in Recurrent Refractory Advanced Gynaecological Cancer: An Experience From the Regional Cancer Centre of Eastern India.Cureus. 2024 Jan 30;16(1):e53232. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53232. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38425585 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Diets with Altered Levels of Sulfur Amino Acids Induce Anticancer Activity in Mice with Metastatic Colon Cancer, Ovarian Cancer and Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 27;24(5):4587. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054587. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902018 Free PMC article.
-
Combination chemotherapy with carboplatin, capecitabine and epirubicin (ECarboX) as second- or third-line treatment in patients with relapsed ovarian cancer: a phase I/II trial.Br J Cancer. 2006 Jan 16;94(1):74-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602879. Br J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16306873 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Blum JL, Dieras V, Lo Russo PM, Horton J, Rutman O, Buzdar A, Osterwalder B (2001) Multicenter, phase II study of capecitabine in taxane-pretreated metastatic breast carcinoma patients. Cancer 92: 1759–1768 - PubMed
-
- Blum JL, Jones SE, Buzdar AU, LoRusso PM, Kuter I, Vogel C, Osterwalder B, Burger HU, Brown CS, Griffin T (1999) Multicenter phase II study of capecitabine in paclitaxel-refractory metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 17: 485–493 - PubMed
-
- Boehmer CH, Jaeger W (2002) Capecitabine in treatment of platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res 22: 439–444 - PubMed
-
- Borner MM, Schoffski P, de Wit R, Caponigro F, Comella G, Sulkes A, Greim G, Peters GJ, van der Born K, Wanders J, de Boer RF, Martin C, Fumoleau P (2002) Patient preference and pharmacokinetics of oral modulated UFT versus intravenous fluorouracil and leucovorin: a randomised crossover trial in advanced colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 38: 349–358 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous