IL-18 cDNA vaccination protects mice from spontaneous lupus-like autoimmune disease
- PMID: 14615579
- PMCID: PMC283566
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2336094100
IL-18 cDNA vaccination protects mice from spontaneous lupus-like autoimmune disease
Abstract
The lupus-like autoimmune syndrome of MRL/Mp-Tnfrsf6lpr (lpr) mice is characterized by progressive lymphadenopathy and autoantibody production, leading to early death from renal failure. Activation of T helper lymphocytes is one of the events in the pathogenesis of the disease in these mice and likely in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Among T helper lymphocyte-dependent cytokines, IFN-gamma plays a pivotal role in the abnormal cell activation and the fatal development of the lpr disease. IL-18, an inducer of IFN-gamma in T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, may contribute to the disease because cells from lpr mice are hypersensitive to IL-18 and express high levels of IL-18. To assess the contribution of IL-18 to the pathogenesis in the animal model, in vivo inhibition of IL-18 was attempted. Young lpr mice were vaccinated against autologous IL-18 by repeated administration of a cDNA coding for the murine IL-18 precursor. Vaccinated mice produced autoantibodies to murine IL-18 and exhibited a significant reduction in spontaneous lymphoproliferation and IFN-gamma production as well as less glomerulonephritis and renal damage. Moreover, mortality was significantly delayed in anti-IL-18-vaccinated mice. These studies support the concept that IL-18 plays a major role in the pathogenesis of the autoimmune syndrome of lpr mice and that a reduction in IL-18 activity could be a therapeutic strategy in autoimmune diseases.
Figures
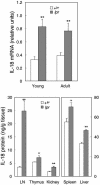



 ) were assessed at weekly intervals starting at 10 weeks of age. Data are from 15–24 mice, tested in three experiments. The difference between control and vaccinated mice was highly significant (P < 0.0001).
) were assessed at weekly intervals starting at 10 weeks of age. Data are from 15–24 mice, tested in three experiments. The difference between control and vaccinated mice was highly significant (P < 0.0001).

 ) are reported (17–18 mice per group in four separate experiments). Survival of IL-18-vaccinated mice was significantly higher than that of control mice (P < 0.0299). Survival of untreated MRL/Mp lpr mice was fully superimposable to that of pEF2-treated mice (data not shown).
) are reported (17–18 mice per group in four separate experiments). Survival of IL-18-vaccinated mice was significantly higher than that of control mice (P < 0.0299). Survival of untreated MRL/Mp lpr mice was fully superimposable to that of pEF2-treated mice (data not shown).Similar articles
-
IL-12 deficiency in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice delays nephritis and intrarenal IFN-gamma expression, and diminishes systemic pathology.J Immunol. 2003 Apr 1;170(7):3915-25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.7.3915. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12646661
-
Lymphocytes from autoimmune MRL lpr/lpr mice are hyperresponsive to IL-18 and overexpress the IL-18 receptor accessory chain.J Immunol. 2001 Mar 15;166(6):3757-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.6.3757. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11238617
-
Roles of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 in murine lupus.J Clin Invest. 1997 Apr 15;99(8):1936-46. doi: 10.1172/JCI119361. J Clin Invest. 1997. PMID: 9109438 Free PMC article.
-
The central and multiple roles of B cells in lupus pathogenesis.Immunol Rev. 1999 Jun;169:107-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01310.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10450512 Review.
-
The roles of B cells in MRL/lpr murine lupus.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997 Apr 5;815:75-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb52046.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997. PMID: 9186641 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-18 cytokine in immunity, inflammation, and autoimmunity: Biological role in induction, regulation, and treatment.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 11;13:919973. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.919973. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid regulates interleukin-37 in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Clin Immunol. 2013 Jan;33(1):111-7. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9791-z. Epub 2012 Sep 9. J Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22961070
-
Expression level of the growth factor progranulin is related with development of systemic lupus erythematosus.Diagn Pathol. 2013 May 23;8:88. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-88. Diagn Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23702100 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of IL-18 Expression Ameliorates Spontaneous Kidney Failure in MRLlpr Mice.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 14;10(10):e0140173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140173. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26465326 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-18 in Inflammatory Kidney Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 1;8:639103. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.639103. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33732720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Theofilopoulos, A. N. & Dixon, F. J. (1981) Immunol. Rev. 55, 179–216. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, P. L. & Eisenberg, R. A. (1991) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 9, 243–269. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe-Fukunaba, R., Brannan, C. I., Copeland, N. G., Jenkins, N. A. & Nagata, S. (1992) Nature 356, 314–317. - PubMed
-
- Bossù, P., Singer, G. G., Andres, P., Ettinger, R., Marshak-Rothstein, A. & Abbas, A. K. (1993) J. Immunol. 151, 7233–7239. - PubMed
-
- Singer, G. G. & Abbas, A. K. (1994) Immunity 1, 365–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

