Pulmonary drug delivery. Part I: physiological factors affecting therapeutic effectiveness of aerosolized medications
- PMID: 14616418
- PMCID: PMC1884307
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01892.x
Pulmonary drug delivery. Part I: physiological factors affecting therapeutic effectiveness of aerosolized medications
Abstract
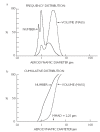
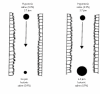
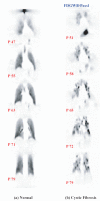
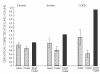
As the end organ for the treatment of local diseases or as the route of administration for systemic therapies, the lung is a very attractive target for drug delivery. It provides direct access to disease in the treatment of respiratory diseases, while providing an enormous surface area and a relatively low enzymatic, controlled environment for systemic absorption of medications. As a major port of entry, the lung has evolved to prevent the invasion of unwanted airborne particles from entering into the body. Airway geometry, humidity, mucociliary clearance and alveolar macrophages play a vital role in maintaining the sterility of the lung and consequently are barriers to the therapeutic effectiveness of inhaled medications. In addition, a drug's efficacy may be affected by where in the respiratory tract it is deposited, its delivered dose and the disease it may be trying to treat.
Figures




References
-
- Dolovich M. New propellant-free technologies under investigation. J Aerosol Med. 1999;12(Suppl 1):s9–s17. - PubMed
-
- Welbanks L, editor. Compendium of pharmaceuticals and specialties. 35. Ottawa, Ontario: CPS Canadian Pharmacists Association; 2000.
-
- Byron PR. Inhalation devices. In: D'Arcy PF, Mcelnay JC, editors. The pharmacy and pharmacotherapy of asthma. Chichester: Ellis Horwood Ltd; 1989. pp. 47–69.
-
- Ruffin RE, Dolovich MB, Wolff RK, Newhouse MT. The effects of preferential deposition of histamine in the human airway. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978;117:485–492. - PubMed
-
- Carstairs JR, Nimmo AJ, Barnes PJ. Autoradiographic visualization of beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in human lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;132:541–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

