Relative paradigms between autoantibodies in lupus and autoantibodies in cancer
- PMID: 14616773
- PMCID: PMC1808856
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02259.x
Relative paradigms between autoantibodies in lupus and autoantibodies in cancer
Figures
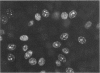
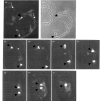
References
-
- Tan EM. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:93–151. - PubMed
-
- Posner JB, Dalmau J. Paraneoplastic syndromes. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:723–924. - PubMed
-
- Musunuru K, Darnell RB. Paraneoplastic neurologic disease antigens: RNA-binding proteins and signaling proteins in neuronal degeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:239–62. - PubMed
-
- Gershwin ME, Manns MP, Mackay IR. Molecular analysis of cytoplasmic autoantigens in liver disease. In: Rose NR, Mackay IR, editors. The autoimmune diseases, II. San Diego: Academic Press; 1992. pp. 213–34.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

