A recombinant fragment of human SP-D reduces allergic responses in mice sensitized to house dust mite allergens
- PMID: 14616775
- PMCID: PMC1808860
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02281.x
A recombinant fragment of human SP-D reduces allergic responses in mice sensitized to house dust mite allergens
Abstract
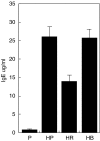
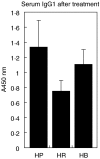
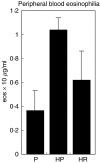
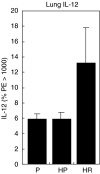
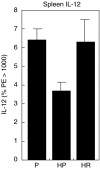
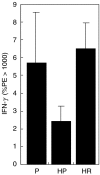
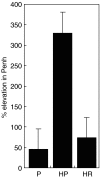
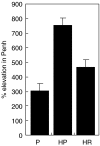
C57Bl6 mice sensitized to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and challenged with D. pteronyssinus allergen extract given intranasally followed by treatment with intranasal applications of a 60-kDa truncated, trimeric recombinant form of human SP-D (rfhSP-D) showed a significant reduction in serum IgE, IgG1, peripheral blood eosinophilia and airway hyperresponsiveness compared to saline or bovine serum albumin-treated controls. Intracellular cytokine staining of lung and spleen homogenates showed increases in interleukin (IL)-12 production in lung tissue and normalization of IL-12 and interferon (IFN)-gamma in spleen tissue. In previous studies we demonstrated the effectiveness of native SP-D and rfhSP-D in down-regulating allergic responses to allergens of Aspergillus fumigatus. The results reported here indicate that rfhSP-D can suppress the development of allergic symptoms in sensitized mice challenged with allergens of the common house dust mite.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intranasal delivery of a truncated recombinant human SP-D is effective at down-regulating allergic hypersensitivity in mice sensitized to allergens of Aspergillus fumigatus.Clin Exp Immunol. 2002 Oct;130(1):19-24. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01968.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12296848 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of a recombinant fragment of human surfactant protein D in a murine model of pulmonary hypersensitivity induced by dust mite allergens.Immunol Lett. 2003 May 1;86(3):299-307. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(03)00033-6. Immunol Lett. 2003. PMID: 12706535
-
Therapeutic effect of surfactant protein D in allergic inflammation of mite-sensitized mice.Clin Exp Allergy. 2005 Apr;35(4):515-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.02205.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005. PMID: 15836762
-
Major house dust mite allergens Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus 1 and Dermatophagoides farinae 1 degrade and inactivate lung surfactant proteins A and D.J Biol Chem. 2007 Dec 21;282(51):36808-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702336200. Epub 2007 Sep 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17848554
-
[House dust mites in the etiology of allergic diseases].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2006;52(2):123-7. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2006. PMID: 17633128 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Innate immune responses to environmental allergens.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2006 Apr;30(2):129-40. doi: 10.1385/criai:30:2:129. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16645224 Review.
-
Therapeutic use of surfactant components in allergic asthma.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;379(3):217-24. doi: 10.1007/s00210-008-0354-z. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18854984 Review.
-
What's new in surfactant? A clinical view on recent developments in neonatology and paediatrics.Eur J Pediatr. 2007 Sep;166(9):889-99. doi: 10.1007/s00431-007-0501-4. Epub 2007 May 22. Eur J Pediatr. 2007. PMID: 17516084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of heterologous production systems for recombinant pulmonary surfactant protein D.Front Immunol. 2014 Dec 8;5:623. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00623. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25538707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural characterisation of ligand-binding determinants in human lung surfactant protein D: influence of Asp325.J Mol Biol. 2009 Dec 11;394(4):776-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.09.057. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19799916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peat JK, Tovey E, Toelle BG, et al. House dust mite allergens. A major risk factor for childhood asthma in Australia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;153:141–6. - PubMed
-
- Platts-Mills TA, Mitchell EB, Chapman MD, Heymann PW. Dust mite allergy: its clinical significance. Hosp Pract (Off, Eds) 1987;22•(91–3):97–100. - PubMed
-
- Sears MR, Herbison GP, Holdaway MD, Hewitt CJ, Flannery EM, Silva PA. The relative risks of sensitivity to grass pollen, house dust mite and cat dander in the development of childhood asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989;19:419–24. - PubMed
-
- Marshall JD, Secrist H, DeKruyff RH, Wolf SF, Umetsu DT. IL-12 inhibits the production of IL-4 and IL-10 in allergen-specific human CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1995;155:111–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

