Abnormal germinal center reactions in systemic lupus erythematosus demonstrated by blockade of CD154-CD40 interactions
- PMID: 14617752
- PMCID: PMC259134
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI19301
Abnormal germinal center reactions in systemic lupus erythematosus demonstrated by blockade of CD154-CD40 interactions
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2007 Mar;117(3):835
Abstract
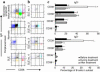
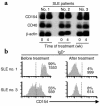
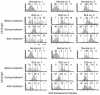
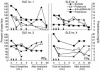
To determine the role of CD154-CD40 interactions in the B cell overactivity exhibited by patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), CD19+ peripheral B cells were examined before and after treatment with humanized anti-CD154 mAb (BG9588, 5c8). Before treatment, SLE patients manifested activated B cells that expressed CD154, CD69, CD38, CD5, and CD27. Cells expressing CD38, CD5, or CD27 disappeared from the periphery during treatment with anti-CD154 mAb, and cells expressing CD69 and CD154 disappeared from the periphery during the post-treatment period. Before treatment, active-SLE patients had circulating CD38 (bright) Ig-secreting cells that were not found in normal individuals. Disappearance of this plasma cell subset during treatment was associated with decreases in anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) Ab levels, proteinuria, and SLE disease activity index. Consistent with this finding, peripheral B cells cultured in vitro spontaneously proliferated and secreted Ig in a manner that was inhibited by anti-CD154 mAb. Finally, the CD38(+/++)IgD(+), CD38(+++), and CD38(+)IgD(-) B cell subsets present in the peripheral blood also disappeared following treatment with humanized anti-CD154. Together, these results indicate that patients with active lupus nephritis exhibit abnormalities in the peripheral B cell compartment that are consistent with intensive germinal center activity, are driven via CD154-CD40 interactions, and may reflect or contribute to the propensity of these patients to produce autoantibodies.
Figures




Comment in
-
Therapeutic CD154 antibody for lupus: promise for the future?J Clin Invest. 2003 Nov;112(10):1480-2. doi: 10.1172/JCI20371. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 14617748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grammer AC, Dorner T, Lipsky PE. Abnormalities in B cell activity and the immunoglobulin repertoire in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Molecular Pathology of Autoimmune Diseases. 2001;2:282–318.
-
- Lipsky PE. Systemic lupus erythematosus: an autoimmune disease of B cell hyperactivity. Nat. Immunol. 2001;2:764–766. - PubMed
-
- Grammer AC, Lipsky PE. CD154-CD40 interactions mediate differentiation to plasma cells in healthy individuals and persons with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1417–1429. - PubMed
-
- Dorner T, Lipsky PE. Immunoglobulin variable-region gene usage in systemic autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2715–2727. - PubMed
-
- Grammer AC, McFarland RD, Heaney J, Darnell BF, Lipsky PE. Expression, regulation, and function of B cell-expressed CD154 in germinal centers. J. Immunol. 1999;163:4150–4159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

