Target-specific utilization of transcriptional regulatory surfaces by the glucocorticoid receptor
- PMID: 14617768
- PMCID: PMC283509
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2336092100
Target-specific utilization of transcriptional regulatory surfaces by the glucocorticoid receptor
Abstract
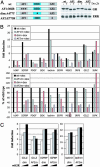
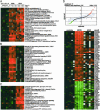
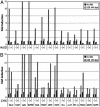
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) activates or represses transcription depending on the sequence and architecture of the glucocorticoid response elements in target genes and the availability and activity of interacting cofactors. Numerous GR cofactors have been identified, but they alone are insufficient to dictate the specificity of GR action. Furthermore, the role of different functional surfaces on the receptor itself in regulating its targets is unclear, due in part to the paucity of known target genes. Using DNA microarrays and real-time quantitative PCR, we identified genes transcriptionally activated by GR, in a translation-independent manner, in two human cell lines. We then assessed in U2OS osteosarcoma cells the consequences of individually disrupting three GR domains, the N-terminal activation function (AF) 1, the C-terminal AF2, or the dimer interface, on activation of these genes. We found that GR targets differed in their requirements for AF1 or AF2, and that the dimer interface was dispensable for activation of some genes in each class. Thus, in a single cell type, different GR surfaces were used in a gene-specific manner. These findings have strong implications for the nature of gene response element signaling, the composition and structure of regulatory complexes, and the mechanisms of context-specific transcriptional regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Ito, M. & Roeder, R. G. (2001) Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 12, 127–134. - PubMed
-
- Levine, M. & Tjian, R. (2003) Nature 424, 147–151. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto, K. R., Darimont, B. D., Wagner, R. L. & Iniguez-Lluhi, J. A. (1998) Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 63, 587–598. - PubMed
-
- Lefstin, J. A. & Yamamoto, K. R. (1998) Nature 392, 885–888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

